Analyzing students’ errors in solving HOTS mathematics problems based on Newman theory
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/ijei.v4i2.9321Keywords:
Newmann theory, HOTS problems, students' errorsAbstract
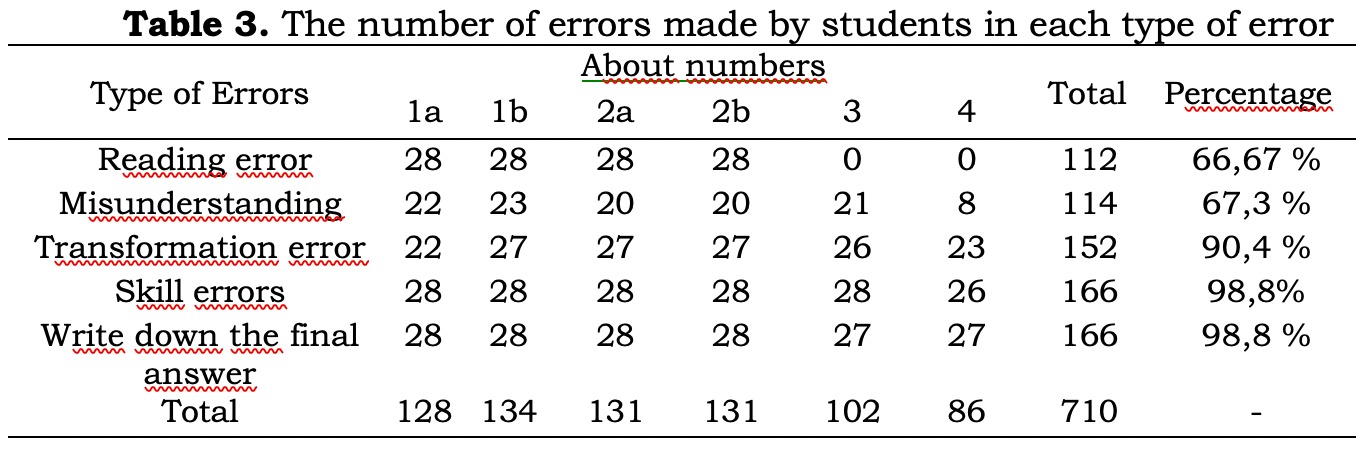
This research is motivated by the existence of the 2013 curriculum, students are required to have the ability to solve problems independently. In supporting this, the strategy in the 2013 curriculum is learning to apply HOTS type questions. This is also applied in the Muhammadiyah Boarding School Pleret. However, when students worked on HOTS questions, it was seen that students still made many mistakes in working on HOTS questions. This study aims to: (1) Know the types of errors made by students of class XI MBS Pleret in solving Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Mathematics questions based on Newman's error analysis (2) Know the factors that cause errors in class XI MBS Pleret students in solving problems Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Mathematics. This type of research is descriptive qualitative. The subjects of this study were students of class XI MBS Pleret, while the object of this research was HOTS (High Order Thinking Skill) type questions. Data collection methods are conducting tests and interviews with students. The instruments used in this study were test questions, interviews and documentation. The analytical method used in this study is data reduction, data presentation, and drawing conclusions. The results of this study were (1) Types of errors made by students of class XI MBS Pleret in solving HOTS questions on trigonometry equation material based on Newman's error analysis consisting of reading errors, understanding errors, transformation errors, skills errors, and errors in writing the final answer. Based on the student error percentage table, the most students made mistakes in the process skills of 98.8% and the errors in writing the final answer was 98.8%. Then for the transformation error of 90.4%, the error in understanding is 67.3% and the smallest error is a reading error which is 66.67%. (2) The causal factors are that students do not know the α symbol (reading errors), students are not used to writing and are known and asked questions other than story questions (comprehension errors), students forget the formula to work on HOTS questions (transformation errors), the result of previous mistakes students made process skill errors and mistakes in writing the final answer.
References
Isslamiyah, N. I., & Wijayanti, P. (2022). Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Siswa Sma Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Ditinjau Dari Jenis Kelamin. Mathedunesa, 11(3).
Amah, M. (2021). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Tipe HOTS Berdasarkan Gender pada Materi Program Linear Di Kelas XI SMA Negeri 2 Brebes.
Andreina, M. H. (2019). Analisis High Order Thinking Skill (Hots) Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Open Ended Matematika. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika dan Matematika.
Ayuwirdayana, C. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita Matematika Berdasarkan Prosedur Newman Di Mts N 4 Banda Aceh.
Febriansari, K. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Ditinjau dari Gaya Kognitif.
Halim, S. H., Tahir, S. R., Syahri, A. A., & Husriana. (2021). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Berbasis HOTS Materi Pola Bilangan Berdasarkan Kriteria Hadar. Mandalika Mathematics And Education Journal.
Hasyim, M., & Andreina, F. K. (2019). Analisis High Order Thinking Skill (HOTS) Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Open Ended Matematika. Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika Dan Matematika.
Husriana. (2021). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Berbasis Higher Order Thinking Skills Hots) Berdasarkan Kriteria Hadar Pada Kelas VIII SMP Satap 3 Tellu Limpoe Kabupaten Bone.
Jeharut, E. H., Hariyani, S., & Wulandari, T. C. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Menyelesaikan Soal Cerita Berdasarkan Tahapan Newman Ditinjau Dari Gender. Seminar Nasional FST 2019.
Khalisah, M. N. (2020). Analisis Kemampuan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Higher Order Thinking Skills Ditinjaudari Kemampuan Awal Matematika Dikelas XI IPA SMA N 1 Bukittinggi.
Laman, E. G. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Memecahkan Masalahmatematika Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Berdasarkan Kriteria Hadar Ditinjau dari Kemampuan awal Siswa Kelas XII SMAN 5 Makassar.
Mahmudah, W. (2018). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Bertipe HOTS Berdasar Teori Newman. Jurnal UJMC, 4(1), 49–56.
Mulyani, M., & Muhtadi, D. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Trigonometri Tipe Higher Order Thinking Skillditinjau Dari Gender. JPPM.
Pratiwi, F. (2022). Analisis Kesalahan Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Tipe Hots (Higher Order Thinking Skill) Menggunakan Prosedur Newman Pada Kelas VII SMP Negeri 13 Makassar.
Prishastini, S. (2019). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soalidentitas Trigonometri di Kelas XI Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020.
Rachman, A. F., & Purwasih, R. (2021). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Sma Negeri Di Kota Cimahi Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Matematika Pada Materi Trigonometri. Jurnal Pembelajaran Matematika Inovatif, 4(3).
Ripaldi, M. (2022). Analisis Kemampuan Pemecahan Masalah Matematika Siswa Berbasis HOTS Pada Materi Bangun Ruang di SMP Muhammadiyah 07 Medan.
Savitri, D. A., & Yuliani, A. (2020). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Permasalahan Trigonometri Ditinjau Dari Gender Berdasarkan Newman. Jurnal Pembelajaran Matematika Inovatif, 3(5).
Siswandi, E., Sujadi, I., & Riyadi. (2016). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Masalah Matematika Kontekstual Pada Materisegiempat Berdasarkan Analisis Newman Ditinjau Dari Perbedaan Gender. Jurnal Elektronik Pembelajaran Matematika, 4(7), 633-643.
Yulianti, F., & Novtiar, C. (2021). Analisis Kesalahan Siswa Dalam Menyelesaikan Soal Higher Order Thinking Skill (HOTS) Materi Bangun Ruang Sisi Datar. Jurnal Pembelajaran Matematika Inovatif, 4(6).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Tika Eri Melania, Burhanudin Arif Nurnugroho

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).




