Exploring teachers' strategies in planning in-depth learning of science in junior high school
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/ijei.v7i1.14148Keywords:
deep learning, instructional orchestrator, living systems and cells, metacognitionAbstract
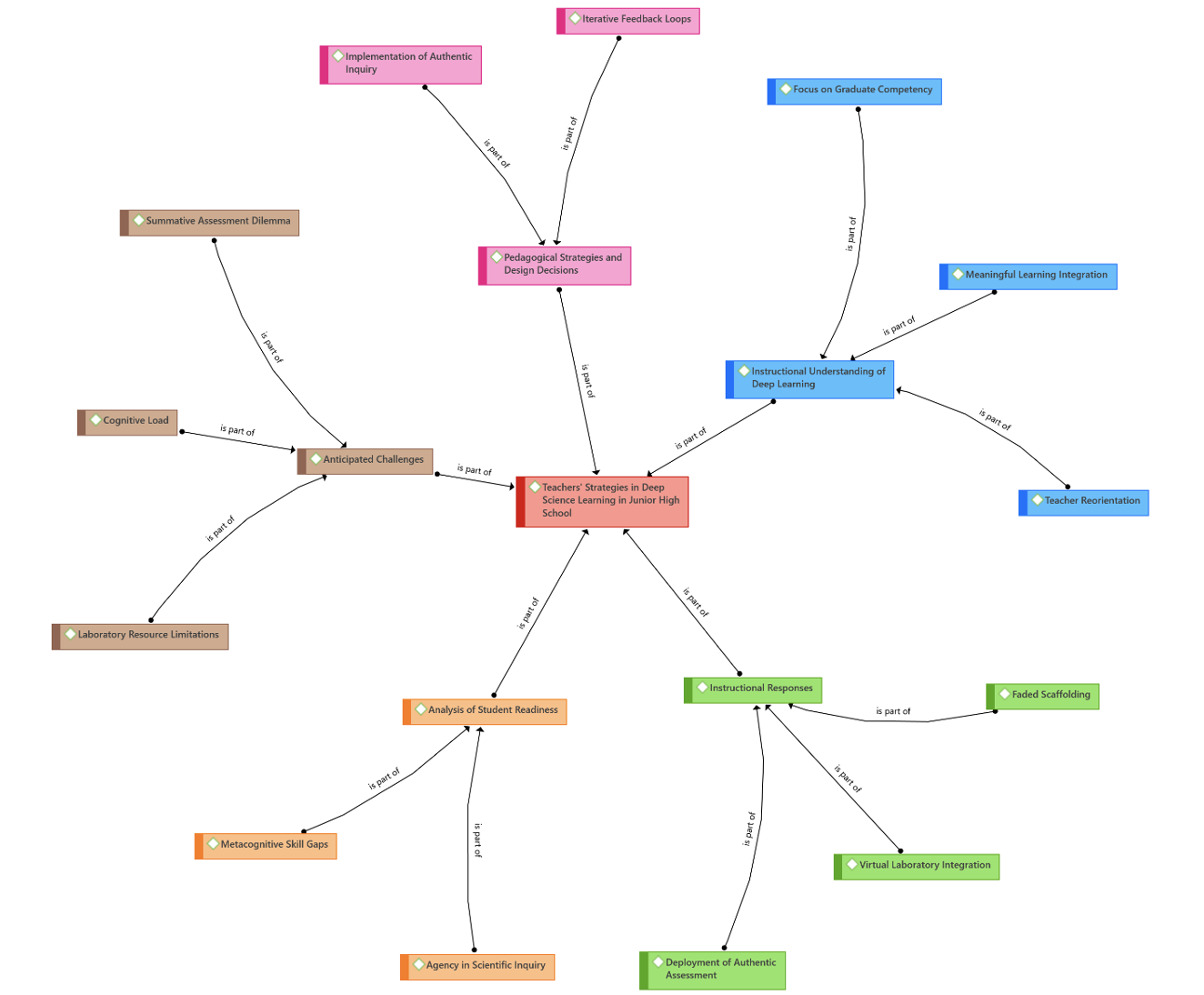
This study aims to construct an effective deep science learning planning model for junior high school teachers on the topic of living systems and cells, focusing on teacher perceptions, student readiness, and the instructional challenges encountered. A descriptive qualitative method was employed, involving in-depth interviews with science teachers and a document study of instructional plans. The findings reveal that deep science learning planning model is contingent upon a fundamental transformation of the teacher’s role into an instructional orchestrator who integrates spiritual dimensions as substantive learning outcomes. While students exhibited metacognitive gaps in navigating experimental inquiry, the study highlights the efficacy of faded scaffolding strategies and virtual laboratory integration in enhancing student self-efficacy amidst resource constraints. The research concludes that despite the systemic tension between time-intensive inquiry and standardized assessments, the adaptation of flexible scaffolding is crucial for bridging scientific reasoning with national testing policies. These results corroborate existing frameworks on deep learning while providing a practical model for teachers in constructing self-identity through an awareness of the Creator’s design in science.
References
Alam, A. (2022). Investigating sustainable education and positive psychology interventions in schools towards achievement of sustainable happiness and wellbeing for 21st century pedagogy and curriculum. ECS Transactions, 107(1), 19481. https://doi.org/ 10.1149/10701.19481ecst
Amini, G. U., Anami, S. F., & Utami, V. N. (2024). Interaksi sains dan agama: Perspektif kimia dalam agama Islam sebagai ilmu pengetahuan dan keimanan. Islamologi: Jurnal Ilmiah Keagamaan, 1(2), 437-448. http://jipkm.com/index.php/islamologi/article/view/183
Artati, K. B., Wahyuni, E., & Fitri, S. (2025). Gambaran Kesejahteraan Psikologis Siswa Kelas Besar Sekolah Dasar dan Implikasinya Terhadap Program Mindfulness Berbasis Sekolah. G-Couns: Jurnal Bimbingan dan Konseling, 9(2), 953-970. https://doi.org/10.31316/g-couns.v9i2.7044
Bergmann, M., Schäpke, N., Marg, O., Stelzer, F., Lang, D. J., Bossert, M., Gantert, M., Häußler, E., Marquardt, E., & Piontek, F. M. (2021). Transdisciplinary sustainability research in real-world labs: success factors and methods for change. Sustainability Science, 16, 541–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11625-020-00886-8
Bråten, O. M. H., & Skeie, G. (2020). Deep learning in studies of religion and worldviews in Norwegian schools? The implications of the national curriculum renewal in 2020. Religions, 11(11), 579. https://doi.org/10.3390/rel11110579
Fullan, M., & Langworthy, M. (2014). A rich seam: How new pedagogies find deep learning. Technical Report. Pearson. https://staging.oer4pacific.org/id/eprint/5/
Hasanah, E., Suyatno, S., Maryani, I., Badar, M. I. Al, Fitria, Y., & Patmasari, L. (2022). Conceptual Model of differentiated-instruction (DI) Based on teachers’ experiences in Indonesia. Education Sciences, 12(10), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12100650
Hasanah, E., Maryani, I., & Gestiardi, R. (2023). Digital-based Differentiation Learning Model in Schools. K-Media.
Hasanah, E. (2024). Managing Personalization and Collaboration in Education: A Systematic Review of Educational Practices. Al-Tanzim: Journal of Islamic Education Management, 8(3), 1043–1055. https://doi.org/10.33650/al-tanzim.v8i3.8751
Hattie, J. (2008). Visible learning: A synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to achievement. Routledge.
Hossain, S., O’neill, S., & Strnadová, I. (2023). What constitutes student well-being: A scoping review of students’ perspectives. Child Indicators Research, 16(2), 447–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-022-09990-w
Juanta, P., Nababan, M. N., Sijabat, A., Yohandri, Y., & Festiyed, F. (2023). Penerapan model pembelajaran inquiry training untuk meningkatkan keterampilan proses sains (KPS) IPA Fisika siswa kelas VII SMP. Jurnal Muara Pendidikan, 8(1), 204-208. https://doi.org/10.52060/mp.v8i1.1041
Kusuma, Y. Y., & Sumianto, S. (2022). Pengembangan model manajemen pelatihan pembuatan bahan ajar berbasis kearifan lokal bagi guru. Innovative: Journal of Social Science Research, 2(2), 35-39. https://j-innovative.org/index.php/Innovative/article/view/72
Malik, R. S. (2018). Educational challenges in 21st century and sustainable development. Journal of Sustainable Development Education and Research, 2(1), 9-20. https://doi.org/10.17509/jsder.v2i1.12266
Mashuri, M., & Hasanah, E. (2021). Manajemen pembelajaran bahasa Inggris dalam meningkatkan hasil belajar siswa saat pandemi COVID-19 di SMA Muhammadiyah 3 Yogyakarta. Diglosia: Jurnal Kajian Bahasa, Sastra, dan Pengajarannya, 4(2), 227-234. https://doi.org/10.30872/diglosia.v4i2.174
Mehta, J., & Fine, S. (2019). In search of deeper learning: The quest to remake the American high school. Harvard University Press.
Norrizqa, H. (2021). Berpikir kritis dalam pembelajaran IPA. In Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan IPA. https://jbse.ulm.ac.id/index.php/PMPIPA/article/view/37
Nugraha, I. P. R., & Nurita, T. (2021). Penerapan model pembelajaran inkuiri untuk meningkatkan keterampilan proses sains (KPS) siswa SMP. Pensa E-Jurnal: Pendidikan Sains, 9(1), 67–71. https://doi.org/10.26740/pensa.v9i1.38503
Sabrina, M., Hairani, M., & Syahrial, S. (2024). Pengembangan model pembelajaran kolaboratif antara guru dan orang tua dalam mendukung kemajuan belajar siswa di sekolah dasar. Dinamika Pembelajaran: Jurnal Pendidikan dan Bahasa, 1(2), 55-67. https://doi.org/10.62383/dilan.v1i2.117
Saldaña, J. (2021). Coding techniques for quantitative and mixed data. The Routledge reviewer’s guide to mixed methods analysis, 151-160.
Siregar, T. (2023). Stages of research and development model research and development (R&D). DIROSAT: Journal of Education, Social Sciences & Humanities, 1(4), 142-158. https://doi.org/10.58355/dirosat.v1i4.48
Sukristin, S., Sabaryati, J., Akbar, A., & Sulestry, A. I. (2025). Developing pedagogical innovation: AI-based deep learning training in elementary education. Jurnal Pedagogi dan Inovasi Pendidikan, 1(3), 1-7. https://jurnal-pip.com/index.php/jpip/article/view/16
Thiers, N. (2017). Making progress possible: A conversation with Michael Fullan. Educational Leadership, 74(9), 8-14. https://michaelfullan.ca/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/Michael-Fullan-Educational-Leadership-Six-Secrets-Interview.pdf
Tifani, A., & Dewi, N. R. (2023). Penerapan model problem based learning untuk meningkatkan keterampian sosial peserta didik kelas VIII E SMP N 41 Semarang. In Proceeding Seminar Nasional IPA (pp. 456-465). Universitas Negeri Semarang. https://proceeding.unnes.ac.id/snipa/article/view/2327/1795
Yusmar, F., & Fadilah, R. E. (2023). Analisis rendahnya literasi sains peserta didik Indonesia: Hasil PISA dan faktor penyebab. LENSA (Lentera Sains): Jurnal Pendidikan IPA, 13(1), 11-19. https://doi.org/10.24929/lensa.v13i1.283
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2026 Kawit Sayoto, Enung Hasanah, Muhammad Zuhaery, Russasmita Sri Padmi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).




