A New Adaptive Flux-Oriented Control Framework for Induction Motors with Online Neural Network Training
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v7i3.13727Keywords:
Torque Ripple Reduction, Online RBF Network, MRAS-based Neural Adaptation, Flux-Oriented Control, Real-Time Adaptive ControlAbstract
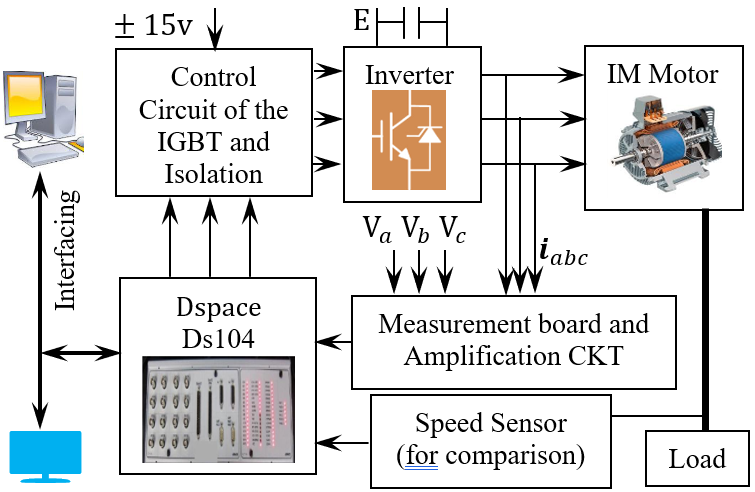
Unlike conventional field oriented control methods, this paper presents a mathematically novel control strategy for induction motor drives, formulated using a two-loop nonlinear dynamic inversion (NDI) framework inspired by aeronautical control architectures. Sensorless operation is realized with a conventional rotor flux observer, while several additional enhancements are introduced to raise overall performance. In particular, a real time radial basis function (RBF) neural network is systematically embedded in a model reference adaptive system (MRAS), replacing the traditional PI adaptation loop with an online training mechanism that improves speed estimation accuracy under parameter variations and load disturbances. The single layer RBF network is trained by gradient descent and incorporated into the nonlinear observer without compromising closed loop stability. The complete controller was implemented on a 1.1 kW, 1430 rpm induction motor using a dSPACE DS1104 real time platform. Experimental results show clear superiority over classical FOC as well as DTSFC and DTRFC schemes, achieving the lowest measured flux ripple (0.002 Wb), minimal torque ripple (0.043 N·m), and the fastest torque response time (0.65 ms). The steady state speed error was reduced by 91 % (from 0.65 to 0.08 rad/s), settling times remained below 60 ms, and both RMSE and ISE metrics decreased appreciably across all tested conditions. Although the proposed design incurs moderate computational overhead, it is fully compatible with real time execution. Future work will examine scalability to high power drives, improved resilience to temperature induced parameter drift, and adaptation of the NDI based framework to permanent magnet machines.
References
A. Bennassar, A. Abbou, and M. Akherraz, “Combining fuzzy Luenberger observer and Kalman filter for speed sensorless integral backstepping controlled induction motor drive,” International Journal of Automation and Control, vol. 11, no. 3, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1504/IJAAC.2017.084871.
A. Rihar et al., “Emerging Technologies for Advanced Power Electronics and Machine Design in Electric Drives,” Applied Sciences, vol. 14, no. 24, p. 11559, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/app142411559.
F. Shiravani, P. Alkorta, J. A. Cortajarena, and O. Barambones, “An Enhanced Sliding Mode Speed Control for Induction Motor Drives,” Actuators, vol. 11, no. 1, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/act11010018.
P. M. Menghal and A. J. Laxmi, “Neural network based dynamic simulation of induction motor drive,” in 2013 International Conference on Power, Energy and Control (ICPEC), pp. 566–571, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPEC.2013.6527722.
U. Sengamalai, G. Anbazhagan, T. M. Thamizh Thentral, P. Vishnuram, T. Khurshaid, and S. Kamel, “Three Phase Induction Motor Drive: A Systematic Review on Dynamic Modeling, Parameter Estimation, and Control Schemes,” Energies, vol. 15, no. 21, p. 8260, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/en15218260.
H. Kubota, K. Matsuse, and T. Nakano, “DSP-Based Speed Adaptive Flux Observer of Induction Motor,” IEEE Trans Ind Appl, vol. 29, no. 2, 1993, https://doi.org/10.1109/28.216542.
N. Medjadjii, A. Chaker, and D. M. Medjahed, “Quality improvement of speed estimation in induction motor drive by using fuzzy-MRAS observer with experimental investigation,” International Review of Automatic Control, vol. 11, no. 1, 2018, https://doi.org/10.15866/ireaco.v11i1.14425.
Q. Sun, Y. Zhang, S. Wu, C. Zhang, and X. Wang, “Adaptive Robust Control of an Industrial Motor-Driven Stage with Disturbance Rejection Ability Based on Multidimensional Taylor Network,” Applied Sciences (Switzerland), vol. 13, no. 22, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/app132212231.
X. Liu, S. Zhen, F. Wang, and M. Li, “Adaptive robust control of the PMSM servo system with servo and performance constraints,” Journal of Vibration and Control, p. 10775463241278003, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1177/10775463241278003.
Z. Mekrini and B. Seddik, “Fuzzy logic application for intelligent control of an asynchronous machine,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 7, no. 1, 2017, https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v7.i1.
W. Hamdi, M. Y. Hammoudi, and A. Betka, “Sensorless Speed Control of Induction Motor Using Model Reference Adaptive System and Deadbeat Regulator,” Engineering Proceedings, vol. 56, no. 1, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/ASEC2023-15240.
K. N. Sujatha and K. Vaisakh, “Implementation of Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System in Speed Control of Induction Motor Drives,” Journal of Intelligent Learning Systems and Applications, vol. 02, no. 02, 2010, https://doi.org/10.4236/jilsa.2010.22014.
P. Stewart, D. A. Stone, and P. J. Fleming, “Design of robust fuzzy-logic control systems by multi-objective evolutionary methods with hardware in the loop,” Eng Appl Artif Intell, vol. 17, no. 3, 2004, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2004.03.003.
T. Takagi and M. Sugeno, “Fuzzy Identification of Systems and Its Applications to Modeling and Control,” IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern, vol. SMC-15, no. 1, 1985, https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399.
B. Bekhiti, B. Nail, I. E. Tibermacine, and R. Salim, “On Hyper‐Stability Theory Based Multivariable Nonlinear Adaptive Control: Experimental Validation on Induction Motors,” IET Electr Power Appl, vol. 19, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1049/elp2.70035.
B. Bekhiti, B. Nail, and A. Kouzou, “Adaptive senssorless control of a feedback linearized induction motor via the extended kalman filter,” In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Power Electronics and Their Applications (ICPEA'15), 2015, https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Belkacem-Bekhiti/publication/274566711_Adaptive_Sensorless_Control_of_a_Feedback_Linearised_Induction_Motor_via_Extended_Kalman_Filter/.
B. Bekhiti, A. Dahimene, and K. Hariche, Advanced nonlinear control and state observation in robotics. Scholars’ Press, Igors Ivanovs, 2017, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/314114908_Advanced_nonlinear_control_and_state_observation_in_robotics.
A. A. Mostfa, N. A. Zakar, R. Raad Al-Mola, and A.-N. Sharkawy, “Enhancing Wind Turbine Power Output Estimation Using Causal Inference and Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System ANFIS,” Kufa Journal of Engineering, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 400–422, Apr. 2025, https://doi.org/10.30572/2018/KJE/160224.
I. A. Kheioon, R. Al-Sabur, and A.-N. Sharkawy, “Design and Modeling of an Intelligent Robotic Gripper Using a Cam Mechanism with Position and Force Control Using an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Computing Technique,” Automation, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 4, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/automation6010004.
A. S. Bahedh, I. A. Kheioon, B. S. Munahi and R. Al-Sabur, "Modelling and controlling of modified robotic gripper mechanism using intelligent technique scheme," 2022 Iraqi International Conference on Communication and Information Technologies (IICCIT), pp. 252-257, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/IICCIT55816.2022.10010666.
D. D. Saputra, A. Ma, H. Maghfiroh, M. A. Baballe, and A. Marcelo, “Performance Evaluation of Sliding Mode Control ( SMC ) for DC Motor Speed Control,” Jurnal Ilmiah Teknik Elektro Komputer dan Informatika (JITEKI), vol. 9, no. 2, 2023, https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v9i2.26291.
M. H. Sabzalian et al., “A Neural Controller for Induction Motors: Fractional-Order Stability Analysis and Online Learning Algorithm,” Mathematics, vol. 10, no. 6, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/math10061003.
M. A. Denaï and S. A. Attia, “Intelligent Control of an Induction Motor,” Electric Power Components and Systems, vol. 30, no. 4, pp. 409–427, 2002, https://doi.org/10.1080/15325000252888010.
N. Pimkumwong and M. S. Wang, “Online speed estimation using artificial neural network for speed sensorless direct torque control of induction motor based on constant V/F control technique,” Energies (Basel), vol. 11, no. 8, 2018, https://doi.org/10.3390/en11082176.
A. A. Bohari, W. M. Utomo, Z. A. Haron, N. Muhd. Zin, S. Y. Sim, and R. M. Ariff, “Speed Tracking of Indirect Field Oriented Control Induction Motor Using Neural Network,” Procedia Technology, vol. 11, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2013.12.173.
M. Demirtas, E. Ilten, and H. Calgan, “Pareto-Based Multi-objective Optimization for Fractional Order PI λ Speed Control of Induction Motor by Using Elman Neural Network,” Arab J Sci Eng, vol. 44, no. 3, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3364-2.
P. Brandstetter and M. Kuchar, “Sensorless control of variable speed induction motor drive using RBF neural network,” Journal of Applied Logic, vol. 24, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jal.2016.11.017.
H. Saleeb, R. Kassem, “Artificial neural networks applied on induction motor drive for an electric vehicle propulsion system,” Electrical Engineering, vol. 104, no. 3, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00202-021-01418-y.
H. Acikgoz, “Real-time adaptive speed control of vector-controlled induction motor drive based on online-trained Type-2 Fuzzy Neural Network Controller,” International Transactions on Electrical Energy Systems, vol. 30, no. 12, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12678.
A. B. Sharma, S. Tiwari and B. Singh, "Intelligent Speed Estimation in Induction Motor Drive Control using Feed - Forward Neural Network Assisted Model Reference Adaptive System," 2020 IEEE Students Conference on Engineering & Systems (SCES), pp. 1-6, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCES50439.2020.9236736.
S. Hussain and M. A. Bazaz, “Adaptive neural type II fuzzy logic-based speed control of induction motor drive,” in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, pp. 81-92, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7386-1_7.
M. H. Sabzalian, A. Mohammadzadeh, S. Lin, and W. Zhang, “New approach to control the induction motors based on immersion and invariance technique,” IET Control Theory and Applications, vol. 13, no. 10, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-cta.2018.5026.
R. Kumar, S. Das, P. Syam, and A. K. Chattopadhyay, “Review on model reference adaptive system for sensorless vector control of induction motor drives,” IET Electr Power Appl, vol. 9, no. 7, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-epa.2014.0220.
Y. Ren, R. Wang, S. J. Rind, P. Zeng, and L. Jiang, “Speed sensorless nonlinear adaptive control of induction motor using combined speed and perturbation observer,” Control Eng Pract, vol. 123, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conengprac.2022.105166.
J. C. Travieso-Torres and M. A. Duarte-Mermoud, “Normalized Model Reference Adaptive Control Applied to High Starting Torque Scalar Control Scheme for Induction Motors,” Energies (Basel), vol. 15, no. 10, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103606.
I. D. Mienye, T. G. Swart, and G. Obaido, “Recurrent Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Review of Architectures, Variants, and Applications,” Information, vol. 15, no. 9, p. 517, Aug. 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/info15090517.
V. S. Lalapura, V. R. Bhimavarapu, J. Amudha, and H. S. Satheesh, “A Systematic Evaluation of Recurrent Neural Network Models for Edge Intelligence and Human Activity Recognition Applications,” Algorithms, vol. 17, no. 3, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/a17030104.
X. Wu, B. Xiang, H. Lu, C. Li, X. Huang, and W. Huang, “Optimizing Recurrent Neural Networks: A Study on Gradient Normalization of Weights for Enhanced Training Efficiency,” Applied Sciences, vol. 14, no. 15, p. 6578, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/app14156578.
G. C. Verghese and S. R. Sanders, “Observers For Flux Estimation In Induction Machines,” IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 35, no. 1, 1988, https://doi.org/10.1109/41.3067.
A. De Luca and G. Ulivi, “Dynamic decoupling of voltage frequency controlled induction motors,” pp. 127–137, 1988, https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0042208.
H. Xie, F. Wang, W. Zhang, C. Garcia, J. Rodríguez and R. Kennel, "Sliding Mode Flux Observer Based Predictive Field Oriented Control for Induction Machine Drives," 2020 IEEE 9th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC2020-ECCE Asia), pp. 3021-3025, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/IPEMC-ECCEAsia48364.2020.9368086.
A. G. Zinyagin, A. V. Muntin, V. S. Tynchenko, P. I. Zhikharev, N. R. Borisenko, and I. Malashin, “Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)-Based Approach to Predict Mean Flow Stress in Industrial Rolling,” Metals (2075-4701), vol. 14, no. 12, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121329.
C. H. Yu, et al., “Recurrent neural network methods for extracting dynamic balance variables during gait from a single inertial measurement unit,” Sensors, vol. 23, no. 22, p. 9040, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/s23229040.
D. Utebayeva, L. Ilipbayeva, and E. T. Matson, “Practical study of recurrent neural networks for efficient real-time drone sound detection: A review,” Drones, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 26, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/drones7010026.
R. Pascual, M. Esteban, J. M. Guerrero, and C. A. Platero, “Recurrent Neuronal Networks for the Prediction of the Temperature of a Synchronous Machine During Its Operation,” Machines, vol. 13, no. 5, p. 387, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13050387.
A. J. Abougarair, M. K. Aburakhis, and M. M. Edardar, “Adaptive neural networks based robust output feedback controllers for nonlinear systems,” International Journal of Robotics and Control Systems, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 37-56, 2022, https://doi.org/10.31763/ijrcs.v2i1.523.
N. T. Pham, and P. D. Nguyen, “A Novel Hybrid Backstepping and Fuzzy Control for Three Phase Induction Motor Drivers,” International Journal of Robotics & Control Systems, vol. 5, no. 1, 2025, https://doi.org/10.31763/ijrcs.v5i1.1707.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Belkacem Bekhiti, Raheem Al-Sabur , Abdel-Nasser Sharkawy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


