Construction and Implementation of a Digital System for Logistics Majors from the Perspective of Smart Education
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/spekta.v5i1.9721Keywords:
teaching reform , smart education , mathematical transformationAbstract
Background: Faced with the new demand for logistics engineering talents in the modern logistics industry's mathematical transformation and upgrading, building an applied logistics engineering talent training system that meets the requirements of the new era is a key task of current teaching reform.
Contribution: The contribution of this experiment is focuses on the current situation of school enterprise integration in school logistics engineering construction, and proposes a construction.
Method: This experiment using framework method to strengthen the logistics engineering profession, clarify integration goals, build targeted curriculum systems, establish assessment and evaluation frameworks, and improve the mechanism of industry education integration.
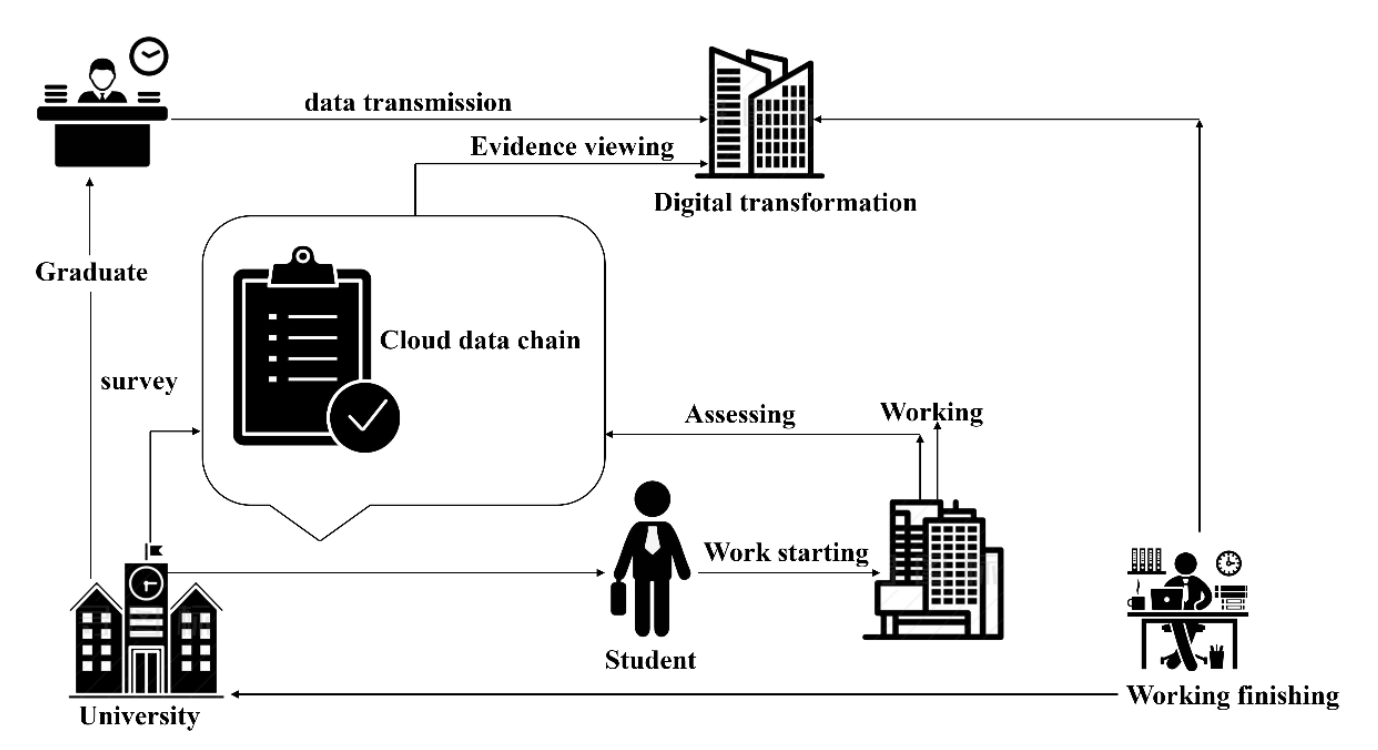
Results: The collaborative educational role of logistics professional construction and innovation and entrepreneurship education and cultivate more comprehensive logistics professionals. Based on this, this article will conduct a digital system for logistics majors from the perspective of smart education in vocational colleges under the background of intelligent logistics.
Conclusion: Curriculum construction is built on a dynamic and authentic practical process, which reflects the logical interaction between curriculum builders and courses, shifting understanding from project logic to subjective logic
References
Moldagulova, A., Satybaldiyeva, R. and Kuandykov, A. “Application of big data in Logistics", Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Engineering & MIS 2020, doi : 10.1145/3410352.3410785
P. Yang and Z. Liu, “The Influence of Immersive Virtual Reality (IVR) on Skill Transfer of Learners: The Moderating Effects of Learning Engagement,” International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Learning/International Journal: Emerging Technologies in Learning, vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 62–73, May 2022, doi: 10.3991/ijet.v17i10.30923
B. Fabian, et al. "Process analysis of a teaching and learning factory environment to demonstrate Industry 4.0 solutions by using the Smart Logistics Zone approach." 2022 IEEE 6th International Conference on Logistics Operations Management (GOL). IEEE, 2022, doi: 10.1109/GOL53975.2022.9820054
L. Cen, D. Ruta, and J. Ng, “Big education: Opportunities for Big Data analytics,” Jul. 2015, doi: 10.1109/icdsp.2015.725192
Woschank, Manuel, et al. "The integration of smart systems in the context of industrial logistics in manufacturing enterprises." Procedia computer science 200 (2022): 727-737, doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2022.01.271
Z. Li, “Research on Accounting Teaching Reform under the Background of Informatization,” Jul. 2019, doi: 10.1145/3349341.3349508
D. M. Z. Islam, J. F. Meier, P. T. Aditjandra, T. H. Zunder, and G. Pace, “Logistics and supply chain management,” Research in Transportation Economics, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 3–16, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.retrec.2012.10.006
N. Y. Li, “Research on the Application of Big Data in Logistics Management,” Management Studies, vol. 9, no. 6, Dec. 2021, doi: 10.17265/2328-2185/2021.06.008
Omonayajo, Babatomiwa, F. Al-Turjman, and N. Cavus. "Interactive and innovative technologies for smart education." Computer science and information systems 19.3 (2022): 1549-1564, doi: 10.2298/CSIS210817027O
L. Gang, et al. "Research on smart campus architecture based on the six domain model of the internet of things." Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Vol. 1861. No. 1. IOP Publishing, 2021, doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1861/1/012038
C. Semeraro, M. Lezoche, H. Panetto, and M. Dassisti, “Digital twin paradigm: A systematic literature review,” Computers in Industry, vol. 130, p. 103469, Sep. 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2021.103469.
L. Koh, A. Dolgui, and J. Sarkis, “Blockchain in transport and logistics – paradigms and transitions,” International Journal of Production Research, vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 2054–2062, Apr. 2020, doi: 10.1080/00207543.2020.1736428.
N. Nordin, A. Khatibi, and S. M. F. Azam, “Nonprofit capacity and social performance: mapping the field and future directions,” Management Review Quarterly, vol. 74, no. 1, pp. 171–225, Sep. 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11301-022-00297-2.
W. Li, K. Bakshi, Y. Tan, and X. Huang, “Policies for Recruiting Talented Professionals from the Diaspora: India and China Compared,” International Migration, vol. 57, no. 3, pp. 373–391, May 2018, doi: 10.1111/imig.12456.
D. Moher, “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement,” Annals of Internal Medicine, vol. 151, no. 4, p. 264, Aug. 2009, doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135.
Ganguly, A. Talukdar, and D. Chatterjee, “Evaluating the role of social capital, tacit knowledge sharing, knowledge quality and reciprocity in determining innovation capability of an organization,” Journal of Knowledge Management, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1105–1135, Aug. 2019, doi: 10.1108/jkm-03-2018-0190
N. S. M. Nabil, H. Nordin, and F. A. Rahman, “Immersive language learning: evaluating augmented reality filter for ESL speaking fluency teaching,” Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1108/jrit-04-2024-0111.
S. Wadhwa and S. Sahoo, “Intellectual capital and subscription rate: an empirical investigation in the Indian initial public offering market,” Accounting Research Journal, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1108/arj-10-2023-0284.
M. N. Khan, P. Akhtar, L. L. Zhang, and Z. Khan, “Operating in environments affected by uncertainty: Supply chain finance, timely information sharing using advanced technology, and financial performance in Supply Chain Management 4.0,” Journal of General Management, Jun. 2024, doi: 10.1177/03063070241263155.
I. Borisenoka, “Opportunities and Barriers to the Delivery of Place-based Environmental Education During Emergency and Non-emergency Teaching: An Information and Communication Technology Approach,” Jun. 2024, doi: 10.32920/26053093.v1.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Lingqun Zuo

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with SPEKTA (Jurnal Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat: Teknologi dan Aplikasi) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.












