Proximate and Texture Profile Analysis of Gluten-Free Cookies Made from Black Glutinous Rice and Mung Bean Flour
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/jafost.v6i2.12717Keywords:
Black glutinous rice, Cookies, Mung bean, Proximate, Texture profileAbstract
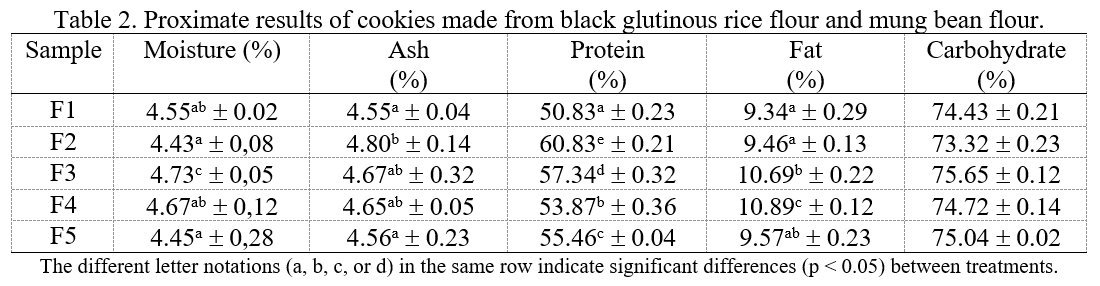
Cookies are one of the food product kinds that have been extensively studied as low-calorie and high-fiber foods. Non-gluten cookies (high fiber) could be made with black glutinous flour and mung bean flour. Black glutinous rice is a valuable ingredient to enhance dietary fiber and antioxidants in food products. The mung bean flour had significant levels of crude fiber (3.77%), iron (89.62 mg), and protein (18.42%). This substance was chosen because mung bean flour and black glutinous rice flour are gluten-free flour, and this research contributed to diversifying food beyond grains and cereal and analyzing that physicochemical profile. This study offers to determine the differences between the findings of proximate analysis and texture profile analysis in cookies made using mung bean flour and black glutinous rice flour. The composite of flour was made from mung black glutinous rice flour and mung bean (F1 = 0:100; F2 = 30:70; F3 = 70:30; F4 = 100:0). The experiment used a completely randomized design to compare the physicochemical and profile texture parameters of cookies. The result of this study is the highest proximate content in terms of protein is in F2, with a moisture content of 4.43%, ash content of 4.80, fat content of 9.46, and carbohydrate content of 73.32%, which is following the Indonesian National Standard (SNI) 01-2973-2022. The texture profile such as hardness 106.23 ± 0.12 N, cohesiveness 0.405 ± 0.17, springiness 0.84 ± 0.24, gumminess 53.54 ± 0.04, and chewiness 33.53 ± 0.02 N.
References
M. Garrido-Romero, A. Montilla, and F. J. Moreno, “Dietary carbohydrates: A trade-off between appealing organoleptic and physicochemical properties and ability to control glucose release and weight management,” Curr. Opin. Food Sci., vol. 49, p. 100976, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2022.100976.
S. Z. Asadi, M. A. Khan, and S. Zaidi, “A study on the shelf life of cookies incorporated with sapota and beetroot leaf powders,” J. Food Sci. Technol., vol. 59, no. 10, pp. 3848–3856, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05408-1.
Y. Zhang, J. Zhou, W. Tian, Y. Gui, and Y. Li, “Effects of soy flour formulation and pretreatment on the properties of gluten-free cookies: A comprehensive study from flour, dough, to baked products,” Food Chem., vol. 468, p. 142481, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.142481.
M. Das, U. Dash, S. S. Mahanand, P. K. Nayak, and R. K. Kesavan, “Black rice: A comprehensive review on its bioactive compounds, potential health benefits and food applications,” Food Chem. Adv., vol. 3, p. 100462, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2023.100462.
M. Ramos, E. Laveriano, L. San Sebastián, M. Perez, A. Jiménez, R. M. Lamuela-Raventos, M. C. Garrigós, and A. Vallverdú-Queralt, “Rice straw as a valuable source of cellulose and polyphenols: Applications in the food industry,” Trends Food Sci. Technol., vol. 131, pp. 14–27, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2022.11.020.
A. Ansari, A. Pranesti, M. Telaumbanua, T. Alam, Taryono, R. A. Wulandari, B. D. A. Nugroho, and Supriyanta, “Evaluating the effect of climate change on rice production in Indonesia using multimodelling approach,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 9, p. e19639, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19639.
M. A. Rahim, M. Umar, A. Habib, M. Imran, W. Khalid, C. M. G. Lima, A. Shoukat, N. Itrat, A. Nazir, A. Ejaz, A. Zafar, C. G. Awuchi, R. Sharma, R. F. Santana, and T. Bin Emran, “Photochemistry, functional properties, food applications, and health prospective of black rice,” J. Chem., vol. 2022, pp. 1–21, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/2755084.
C. Loyda, R. Singanusong, A. Jaranrattanasri, and W. Tochampa, “Physicochemical characterization of broken rice and analysis of its volatile compounds,” Walailak J. Sci. Technol., vol. 18, no. 6, 2021, https://doi.org/10.48048/wjst.2021.9136.
M.-Y. Kang, C. Rico, and S.-C. Lee, “Physicochemical properties of eight popular glutinous rice varieties in Korea,” Plant Prod. Sci., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 177–184, 2010, https://doi.org/10.1626/pps.13.177.
C. Gunathunga, S. Senanayake, M. A. Jayasinghe, C. S. Brennan, T. Truong, U. Marapana, and J. Chandrapala, “Germination effects on nutritional quality: A comprehensive review of selected cereals and pulses changes,” J. Food Compos. Anal., vol. 128, p. 106024, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2024.106024.
M. M. Ali and N. Hashim, “Exploring nutritional compositions, volatile compounds, health benefits, emerging processing technologies, and potential food products of glutinous rice: A review,” Rice Sci., vol. 31, no. 3, pp. 251–268, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rsci.2024.02.002.
L. M. Devi and L. S. Badwaik, “Variety difference in physico-chemical, cooking, textural, pasting and phytochemical properties of pigmented rice,” Food Chem. Adv., vol. 1, p. 100059, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100059.
D. Gunarti and Josua Kristinao Hilmanto, “Isolation and identification of thiamine-binding protein from black glutinous rice bran (Oryza Sativa var. Glutinosa),” EKSAKTA J. Sci. Data Anal., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 162–170, 2024, https://doi.org/10.20885/EKSAKTA.vol5.iss2.art6.
H. Barakat, R. M. Alhomaid, and R. Algonaiman, “Production and evaluation of kleija-like biscuits formulated with sprouted mung beans,” Foods, vol. 14, no. 9, p. 1571, 2025, https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14091571.
Z. Huang, Y. Li, M. Fan, H. Qian, and L. Wang, “Recent advances in mung bean protein: From structure, function to application,” Int. J. Biol. Macromol., vol. 273, p. 133210, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.133210.
D. Singla, T. Malik, A. Singh, S. Thakur, and P. Kumar, “Advances in understanding wheat-related disorders: A comprehensive review on gluten-free products with emphasis on wheat allergy, celiac and non-celiac gluten sensitivity,” Food Chem. Adv., vol. 4, p. 100627, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2024.100627.
M. G. Shiha, S. Chetcuti Zammit, L. Elli, D. S. Sanders, and R. Sidhu, “Updates in the diagnosis and management of coeliac disease,” Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol., vol. 64–65, p. 101843, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2023.101843.
AOAC, Official Methode of Analysis Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 2005.
D. P. Suleman, M. M. Sari, A. N. Rochmah, and F. Zulfa, “Sensory acceptability and characteristics of cinnamon roll bread with pineapple puree (Ananas comosus L.) substituted with taro flour,” J. Agri-Food Sci. Technol., vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–10, 2025, https://doi.org/10.12928/jafost.v6i1.11004.
S. N. N. Makiyah, I. Setyawati, S. N. Rahmadhia, S. Tasminatun, and M. Kita, “Comparison of yam composite cookies sensory characteristic between sugar and stevia sweeteners,” J. Agri-Food Sci. Technol., vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 120–133, 2024, https://doi.org/10.12928/jafost.v5i2.10211.
A. Mustofa, N. Suhartatik, and E. S. Ningrum, “Antioxidant and anti inflammation effect of snack bars from black glutinous rice and pumpkin powder,” Indones. J. Agric. Res., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 77–88, 2019, https://doi.org/10.32734/injar.v2i3.2841.
Badan Standarisasi Nasional, “Syarat Mutu Cookies SNI 01-2973-2022,” Jakarta: Badan Standarisasi Nasional, 2022.
D. S. Lee and G. L. Robertson, “Shelf‐life estimation of packaged dried foods as affected by choice of moisture sorption isotherm models,” J. Food Process. Preserv., vol. 46, no. 3, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.16335.
N. Salma, A. Setiyoko, Y. P. Sari, and Y. Rahmadian, “Effect of Wheat Flour and Yellow Pumpkin Flour Ratios on The Physical, Chemical Properties, and Preference Level of Cookies,” J. Agri-Food Sci. Technol., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 59–70, 2024, https://doi.org/10.12928/jafost.v4i2.7882.
W. T. Eden and C. O. Rumambarsari, “Proximate analysis of soybean and red beans cookies according to the Indonesian National Standard,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1567, no. 2, p. 022033, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1567/2/022033.
J. M. Sakung, S. Nuryanti, A. Afadil, S. H. V. Pulukadang, M. Maryam, and M. Mar’atun, “Evaluation of proximate and mineral composition of biscuit formulated using chayote (Sechium edule) and mung bean (Vigna radiata) flours,” Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci., vol. 9, no. A, pp. 373–377, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2021.6121.
L. Ratnawati, D. Desnilasari, D. N. Surahman, and R. Kumalasari, “Evaluation of physicochemical, functional and pasting properties of soybean, mung bean and red kidney bean flour as ingredient in biscuit,” IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 251, p. 012026, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/251/1/012026.
M. Kumar, M. Tomar, S. Punia, J. Dhakane-Lad, S. Dhumal, S. Changan, M. Senapathy, M. K. Berwal, V. Sampathrajan, A. A. S. Sayed, D. Chandran, R. Pandiselvam, N. Rais, D. K. Mahato, S. S. Udikeri, et al., “Plant-based proteins and their multifaceted industrial applications,” LWT, vol. 154, p. 112620, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112620.
N. Ajomiwe, M. Boland, S. Phongthai, M. Bagiyal, J. Singh, and L. Kaur, “Protein nutrition: Understanding structure, digestibility, and bioavailability for optimal health,” Foods, vol. 13, no. 11, p. 1771, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13111771.
W. Yan, L. Yin, M. Zhang, M. Zhang, and X. Jia, “Gelatinization, retrogradation and gel properties of wheat starch–wheat bran arabinoxylan complexes,” Gels, vol. 7, no. 4, p. 200, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7040200.
L. Kumar, M. A. Brennan, S. L. Mason, H. Zheng, and C. S. Brennan, “Rheological, pasting and microstructural studies of dairy protein–starch interactions and their application in extrusion‐based products: A review,” Starch - Stärke, vol. 69, no. 1–2, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1002/star.201600273.
N. M. Anbarani, S. M. A. Razavi, and M. Taghizadeh, “Impact of sage seed gum and whey protein concentrate on the functional properties and retrogradation behavior of native wheat starch gel,” Food Hydrocoll., vol. 111, p. 106261, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106261.
S. H. Zafar, M. Umair, and M. Akhtar, “Nutritional evaluation, proximate and chemical composition of mungbean varieties/cultivars pertaining to food quality characterization,” Food Chem. Adv., vol. 2, p. 100160, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100160.
M. Du, J. Xie, B. Gong, X. Xu, W. Tang, X. Li, C. Li, and M. Xie, “Extraction, physicochemical characteristics and functional properties of Mung bean protein,” Food Hydrocoll., vol. 76, pp. 131–140, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.01.003.
V. Campos, L. Tappy, L. Bally, J. L. Sievenpiper, and K.-A. Lê, “Importance of carbohydrate quality: What does it mean and how to measure it?,” J. Nutr., vol. 152, no. 5, pp. 1200–1206, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxac039.
X. Tian, Q. Fang, X. Zhang, S. Yu, C. Dai, and X. Huang, “Visualization of moisture content, reducing sugars, and chewiness in bread during oral processing based on hyperspectral imaging technology,” Foods, vol. 13, no. 22, p. 3589, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/foods13223589.
R. A. Dunne, E. C. Darwin, V. A. Perez Medina, M. E. Levenston, S. R. St. Pierre, and E. Kuhl, “Texture profile analysis and rheology of plant-based and animal meat,” Food Res. Int., vol. 205, p. 115876, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2025.115876.
G. Huang, D. J. McClements, K. He, Z. Zhang, Z. Lin, Z. Xu, Y. Zou, Z. Jin, and L. Chen, “Review of formation mechanisms and quality regulation of chewiness in staple foods: Rice, noodles, potatoes and bread,” Food Res. Int., vol. 187, p. 114459, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114459.
B. Jia, L. Devkota, M. Sissons, and S. Dhital, “Degradation of starch in pasta induced by extrusion below gelatinization temperature,” Food Chem., vol. 426, p. 136524, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136524.
S. N. Rahmadhia, U. N. Saadah, and A. Jebreen, “Physicochemical properties of vegetable leather made from broccoli stems (Brassica oleracea var. italica) with the addition of pectin,” Agrointek J. Teknol. Ind. Pertan., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 436–444, 2025, https://doi.org/10.21107/agrointek.v19i2.25870.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Soraya Kusuma Putri, Agus Setiyoko

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with the Journal of Agri-food Science and Technology (JAFOST) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.



