Physical Quality of Cow's Milk by Exposure to Magnetic Fields Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) 300 μT and 500 μT by inhibiting Salmonella and Escherichia Coli Growth
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/irip.v5i2.5064Keywords:
Escherichia coli , Extremely Low Frequency , Salmonella spAbstract
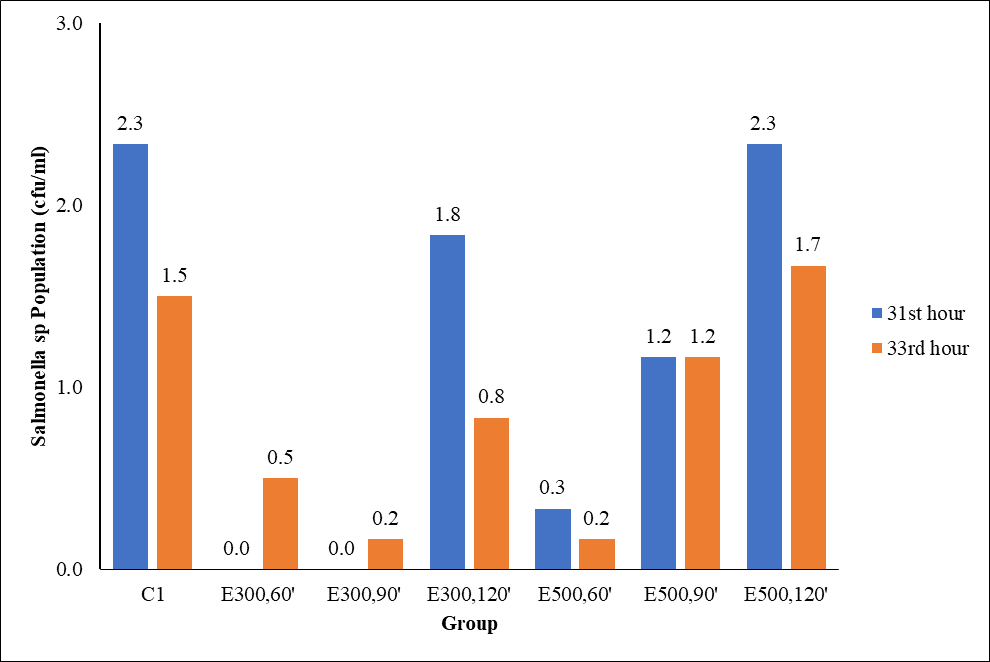
Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) magnetic field, high intensity (more than 100 µT), can suppress the growth of pathogenic bacteria, but the impact of low intensity (≤ 500 µT) needs to be proven. This study aimed to analyze the physical resistance of cow's milk exposed to a magnetic field of 300 µT and 500 µT ELF by inhibiting the proliferation of Salmonella and Escherichia Coli bacteria. Completely Randomized Design (CRD) research design. Samples were 210 bottles of cow's milk (@ 50 ml) divided into seven groups. Exposure to the ELF magnetic field intensity of 300 μT and 500 μT with exposure variations of 60, 90, and 120 minutes. Result: Exposure to an ELF magnetic field with an intensity of 500 µT for 60 minutes significantly (p < 0.05) reduced the Salmonella sp. population but not Escherichia coli. Even though the physical condition showed the color and smell of fresh milk, lumps did not appear until the 10th hour. Conclusion: exposure to the ELF magnetic field intensity of 300 μT and 500 μT has not been able to maintain the quality of cow's milk.
References
Badan Standardisasi Nasional, SNI 3141.1:2011Susu Segar-Bagian 1: Sapi, 1st ed. Jakarta: Badan Standardisasi Nasional, 2011.
K. Salli, J. Hirvonen, J. Siitonen, I. Ahonen, H. Anglenius, and J. Maukonen, “Selective Utilization of the Human Milk Oligosaccharides 2′-Fucosyllactose, 3-Fucosyllactose, and Difucosyllactose by Various Probiotic and Pathogenic Bacteria,” J. Agric. Food Chem., vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 170–182, Jan. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c06041.
Y. Subagyo, R. Olivia, T. Y. Astuti, and P. Soediarto, “Pengkajian Jumlah Mikroba dan Daya Hahan Susu Segar di Kecamatan Sumbang dan Baturraden,” in Prosiding Seminar Teknologi dan Agribisnis Peternakan VII-Webinar: Prospek Peternakan di Era Normal Baru Pasca Pandemi COVID-19, 2020, pp. 532–538, [Online]. Available: http://jnp.fapet.unsoed.ac.id/index.php/psv/article/view/519.
Y. Zakaria, H. M. Yahya, and Y. Safara, “Analisa Kualitas Susu Kambing Peranakan Etawah yang Disterilkan pada Suhu dan Waktu yang Berbeda,” J. Agripet, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 29–31, Apr. 2011, https://doi.org/10.17969/agripet.v11i1.651.
A. Poghossian, H. Geissler, and M. J. Schöning, “Rapid methods and sensors for milk quality monitoring and spoilage detection,” Biosens. Bioelectron., vol. 140, p. 111272, Sep. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.04.040.
M. Kieliszek, K. Pobiega, K. Piwowarek, and A. M. Kot, “Characteristics of the Proteolytic Enzymes Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria,” Molecules, vol. 26, no. 7, p. 1858, Mar. 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071858.
J. Bai et al., “Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts,” Microb. Biotechnol., vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 1171–1182, May 2021, https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13785.
F. Jiang et al., “Treatment of Whole-Plant Corn Silage With Lactic Acid Bacteria and Organic Acid Enhances Quality by Elevating Acid Content, Reducing pH, and Inhibiting Undesirable Microorganisms,” Front. Microbiol., vol. 11, p. 593088, Dec. 2020, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.593088.
A. A. S. Marouf and S. I. Elmhal, “Monitoring pH During Pasteurization of Raw Cow’s Milk using Nd:YAG Laser,” Int. J. Adv. Res. Phys. Sci., vol. 4, no. 12, pp. 1–4, 2017, [Online]. Available: https://www.arcjournals.org/international-journal-of-advanced-research-in-physical-science/volume-4-issue-12/1.
M. Fatmawati et al., “A comparative study among dairy goat breeds in Lumajang and Malang (East Java, Indonesia) based on milk organoleptic and milk composition,” Biodiversitas J. Biol. Divers., vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 2899–2903, Jun. 2022, https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d230616.
Atmanaji, B. S. Hertanto, and A. Pramono, “Physical and hedonic properties of cow milk yogurt containing different levels of avocado pulp (Perseaamericana, Mill),” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 633, no. 1, p. 012049, Oct. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/633/1/012049.
K. Daffner et al., “Design and characterization of casein–whey protein suspensions via the pH–temperature-route for application in extrusion-based 3D-Printing,” Food Hydrocoll., vol. 112, p. 105850, Mar. 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105850.
N. D. Kristanti, D. Rosyidi, Lilik Eka Radiati, and Purwadi, “Phylogenetic tree and heat resistance of thermoduric bacteria isolated from pasteurization milk in Indonesia,” Int. J. Biosci., vol. 6, no. 11, pp. 87–98, Jun. 2015, https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/6.11.87-98.
N. Nikmaram and K. M. Keener, “The effects of cold plasma technology on physical, nutritional, and sensory properties of milk and milk products,” LWT, vol. 154, p. 112729, Jan. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112729.
K. K. Dash et al., “A comprehensive review on heat treatments and related impact on the quality and microbial safety of milk and milk-based products,” Food Chem. Adv., vol. 1, p. 100041, Oct. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2022.100041.
L. F. Paludetti, A. L. Kelly, B. O’Brien, K. Jordan, and D. Gleeson, “The effect of different precooling rates and cold storage on milk microbiological quality and composition,” J. Dairy Sci., vol. 101, no. 3, pp. 1921–1929, Mar. 2018, https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2017-13668.
Sudarti, “Utilization of Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) Magnetic Field is as Alternative Sterilization of Salmonella Typhimurium In Gado-Gado,” Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia, vol. 9, pp. 317–322, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2016.02.140.
Sudarti, B. Supriadi, Subiki, A. Harijanto, Nurhasanah, and Z. R. Ridlo, “A potency of ELF magnetic field utilization to the process of milkfish preservation (chanos chanos),” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 1465, no. 1, p. 012005, Feb. 2020, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1465/1/012005.
L. D. Sari, T. Prihandono, and Sudarti, “Pengaruh Paparan Medan Magnet ELF (Extremely Low Frequency) 500 µT Dan 700 µT terhadap Derajad Keasaman (pH) Daging Ayam.,” Pros. Semin. Nas. Pendidik. Fis., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 195–199, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/fkip-epro/article/view/7397.
K. R. Sadidah, Sudarti, and A. A. Ghani, “Pengaruh Paparan Medan Magnet ELF (Extremely Low Frequency) 300 μT dan 500 μT Terhadap Perubahan Jumlah Mikroba dan pH pada Proses Fermentasi Tape Ketan,” J. Pembelajaran Fis., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 1–8, 2015, [Online]. Available: https://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/JPF/article/view/1733.
Barbosa and Canovas, Oscillating Magnetic Fields for Food Processing. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 1998.
H. L. A. Miñano, A. C. de S. Silva, S. Souto, and E. J. X. Costa, “Magnetic Fields in Food Processing Perspectives, Applications and Action Models,” Processes, vol. 8, no. 7, p. 814, Jul. 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8070814.
E. Bayır, E. Bilgi, A. Şendemir-Ürkmez, and E. E. Hameş-Kocabaş, “The effects of different intensities, frequencies and exposure times of extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7,” Electromagn. Biol. Med., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 14–18, Jan. 2015, https://doi.org/10.3109/15368378.2013.853671.
A. Kristinawati and S. Sudarti, “The Influence of Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) Magnetic Field Exposure on the Process of Making Cream Cheese,” in The 1st IBSC: Towards the Extended Use of Basic Science for Enhancing Health, Environment, Energy and Biotechnology, 2016, pp. 181–183, [Online]. Available: http://jurnal.unej.ac.id/index.php/prosiding/article/view/4191.
D. C. Giancoli, Physics Principles with Applications, Global Edition. England: Pearson Education Limited, 2015.
Y. Wang et al., “Exposure to 50 Hz magnetic field at 100 µT exert no DNA damage in cardiomyocytes,” Biol. Open, Jan. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.041293.
N. N. A. Muharromah, “Pengaruh Paparan Medan Magnet Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) Terhadap pH Susu Sapi Segar sebagai Indikator Kedaluwarsa,” Universitas Jember, 2019.
F. F. Al-Harbi, D. H. M. Alkhalifah, Z. M. Elqahtani, F. M. Ali, S. A. Mohamed, and A. M. M. Abdelbacki, “Nonthermal control of Escherichia coli growth using extremely low frequency electromagnetic (ELF-EM) waves,” Biomed. Mater. Eng., vol. 29, no. 6, pp. 809–820, Nov. 2018, https://doi.org/10.3233/BME-181025.
E. Roza and S. Aritonang, “Pengaruh Lama Penyimpanan Setelah Diperah Terhadap pH, Berat Jenis dan Jumlah Koloni Bakteri Susu Kerbau,” J. Peternak. Indones. (Indonesian J. Anim. Sci., vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 74–78, Feb. 2006, https://doi.org/10.25077/jpi.11.1.74-78.2006.
S. G. Anema, “Age Gelation, Sedimentation, and Creaming in UHT Milk: A Review,” Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf., vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 140–166, Jan. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12407.
S. A. Ferdousi et al., “Water as an Effective Additive for High‐Energy‐Density Na Metal Batteries? Studies in a Superconcentrated Ionic Liquid Electrolyte,” ChemSusChem, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 1700–1711, Apr. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201802988.
S. N. Aritonang, Susu dan Teknologi. Padang: LPTIK Universitas Andalas, 2017.
A. Fatiqin, R. Novita, and I. Apriani, “Pengujian Salmonella dengan Menggunakan Media SSA dan E. Coli Menggunakan Media Emba pada Bahan Pangan,” Indobiosains, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 22–29, Feb. 2019, https://doi.org/10.31851/indobiosains.v1i1.2206.
Warni, “Kualitas Susu Sapi Perah di Kabupaten Sinjai dan Kaitannya dengan Infeksi Listeria Monocytogenes,” Universitas Hasanuddin, 2014.
Sudarti, U. Qumairoh, and T. Prihandono, “The effectiveness of exposure to magnetic fields of extremely low frequency 300T and 500T in inhibiting the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria to increase physical resistance of vannamei shrimp,” J. Phys. Conf. Ser., vol. 2165, no. 1, p. 012038, Jan. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2165/1/012038.
Sudarti, K. Laksmiari, E. Permatasari, and F. W. Ningtyas, “Analysis of Exposure to an Extremely Low Frequency (ELF) 700 μT and 1000 μT Magnetic Fields in Tuna Meat (Euthynnus Affinis C),” J. Sci. Sci. Educ., vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 36–44, 2022, https://doi.org/10.29303/jossed.v3i1.1366.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Sudarti Sudarti, Elok Permatasari, Indri Ratnasari, Sherly Nur Laili

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish in IRiP agree to the following terms: Authors retain copyright and grant the IRiP right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) and adapt (remix, transform, and build upon the material) the work for any purpose, even commercially with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in IRiP. Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in IRiP. Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).














