Investigation of Manufacture Tolerances on Torque Pulsation Profile of Interior Permanent Magnet Motor with Third Harmonic Injected Sinusoidal Rotor Iron Pole
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v8i1.14647Keywords:
Torque Pulsation, Cogging Torque, Interior Permanent Magnet Machine, Rotor Eccentricity, Permanent Magnet DiversityAbstract
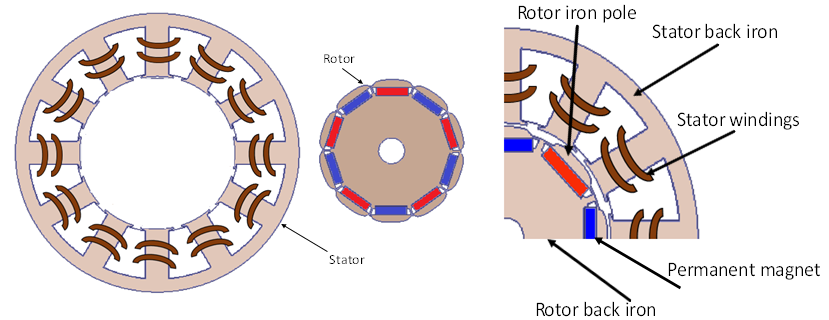
Torque ripple is a significant undesirable aspect of permanent magnet (PM) machine. It is mainly contributed by cogging torque, which is inherit feature of the PM machine. Interior permanent magnet (IPM) motor with a sinusoidal + third-order harmonic injected rotor pole shape has been introduced as one of the most efficient rotor pole arc iron shape techniques to minimize the cogging torque. Such method showed a reduction in the cogging torque compared to the traditional designs. Generally, imperfections in the manufacturing process can exacerbate cogging torque and, by extension, torque ripple. This research assesses how manufacturing tolerances influence the torque ripple of the IPM motor having sinusoidal + third order harmonic rotor pole shape. The investigation has been carried out using two-dimension finite element analysis(2D-FEA) method, ANSOFT MAXWELL program. Different models of the IPMs with sinusoidal + third order harmonic rotor pole shape have been made to simulate healthy, eccentricity and PM diversity cases. According to the simulation results, it has been found that PM diversity leads to introduce additional harmonics in the cogging torque waveforms, i.e., in addition to the fundamental harmonic, which is the 60th harmonic orders, the 12th harmonic and its multiples harmonic orders were presented, consequently resulting in increasing the torque ripple. Moreover, the obtained results have shown that the static eccentricity has more negative effect on the torque ripple compared to the dynamic counterpart, i.e. the torque ripple of the static eccentricity is about 20% higher than that of the dynamic counterpart.
References
M. Sagawa, S. Fujimura, N. Togawa, H. Yamamoto and Y. Matsuura, "New material for permanent magnets on a base of Nd and Fe (Invited)," Journal of Applied Physics, vol. 55, no. 6, pp. 2083-2087, 1984, https://doi.org//10.1063/1.333572.
J. J. Croak, J. F. Herbsf, R. W. Lee, and F. E. Pinkerton, "High- Energy product Nd-Fe-B permanent magnet," Appl. Phys. Lett, vol. 44, no. I, pp. 148-149, 1984, https://doi.org//10.1063/1.94584.
T. Mizoguchi, I. Sakai, H. Niu, and K. Inomata, "Nd-Fe-B-CO-AI based permanent magnets with improved magnetic properties and temperature characteristics," Appl. Phys. Lett., vol.48, no. 5, pp. 1309–1310, 1986, https://doi.org//10.1063/1.96962.
S. Murthy, B. Derouane, B. Liu and T. Sebastian, "Minimization of torque pulsations in a trapezoidal back-EMF permanent magnet brushless DC motor," Conference Record of the 1999 IEEE Industry Applications Conference. Thirty-Forth IAS Annual Meeting (Cat. No.99CH36370), vol. 2, pp. 1237-1242, 1999, https://doi.org/10.1109/IAS.1999.801661.
M. Zheng, Z. Q. Zhu, S. Cai and S. S. Xue, "A Novel Modular Stator Hybrid-Excited Doubly Salient Synchronous Machine With Stator Slot Permanent Magnets," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 1-9, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2019.2902364.
N. Bianchi, E. Fornasiero and W. Soong, "Selection of PM Flux Linkage for Maximum Low-Speed Torque Rating in a PM-Assisted Synchronous Reluctance Machine," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 51, no. 5, pp. 3600-3608, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2015.2416236.
T. Li and G. Slemon, "Reduction of cogging torque in permanent magnet motors," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 2901-2903, 1988, https://doi.org/10.1109/20.92282.
S. Hwang and D. K. Lieu, "Design techniques for reduction of reluctance torque in brushless permanent magnet motors," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 4287-4289, 1994, https://doi.org/10.1109/20.334063.
K. Ohnishi, "Cogging torque reduction in permanent magnet brushless motors" (in Japanese), T. IEE Japan, vol. 122-d, no. 4, 2002, https://doi.org//10.1541/ieejias.122.338.
N. Matumoto, S. Nishimura, M. Sanada, S. Morimoto and Y. Takeda, "Torque performances and arrangement of permanent magnet for IPMSM" (in Japanese), The Papers of Technical Meeting on Rotating Machinery, IEE Japan, RM-04-52, 2004, https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1570572700418166144.
T. M. Jahns and W. L. Soong, "Pulsating torque minimization techniques for permanent magnet ac motor drives: A review," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 43, no. 2, pp. 321-330, 1996, https://doi.org/10.1109/41.491356.
M. S. Islam, S. Mir, and T. Sebastian, "Issues in reducing the cogging torque of mass-produced permanent-magnet brushless DC motor," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 813-820, 2004, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2004.827469.
L. Zhu, S. Z. Jiang, Z. Q. Zhu and C. C. Chan, "Analytical methods for minimizing cogging torque in permanent-magnet machines," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 2023-2031, 2009, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2008.2011363.
S. Leitner, H. Gruebler and A. Muetze, "Cogging Torque Minimization and Performance of the Sub-Fractional HP BLDC Claw-Pole Motor," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 4653-4664, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2019.2923569.
M. García-Gracia, Á. Jiménez Romero, J. Herrero Ciudad, and S. Martín Arroyo, “Cogging Torque Reduction Based on a New Pre-Slot Technique for a Small Wind Generator,” Energies, vol. 11, no. 11, p. 3219, 2018, https://doi.org/10.3390/en11113219.
Z. Goryca, S. Różowicz, A. Różowicz, A. Pakosz, M. Leśko, and H. Wachta, “Impact of Selected Methods of Cogging Torque Reduction in Multipolar Permanent-Magnet Machines,” Energies, vol. 13, no. 22, p. 6108, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/en13226108.
C. Gan, J. Wu, M. Shen, W. Kong, Y. Hu and W. Cao, "Investigation of Short Permanent Magnet and Stator Flux Bridge Effects on Cogging Torque Mitigation in FSPM Machines," IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 845-855, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/TEC.2017.2777468.
J. Gao, Z. Xiang, L. Dai, S. Huang, D. Ni and C. Yao, "Cogging Torque Dynamic Reduction Based on Harmonic Torque Counteract," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 58, no. 2, pp. 1-5, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2021.3093723.
J. R. Hendershot and T. J. E. Miller, "Design of brushless permanent magnet motors," Magna Physics Publishing & Clarendon Press, 1994, https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198593898.001.0001.
N. Levin, S. Orlova, V. Pugachov, B. Ose-Zala, E. Jakobsons, "Methods to Reduce the Cogging Torque in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines,” Electron. Electr. Eng, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 23–26, 2013, https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.eee.19.1.3248.
S. A. Evans, "Salient pole shoe shapes of interior permanent magnet synchronous machines," The XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines - ICEM 2010, pp. 1-6, 2010, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICELMACH.2010.5607694.
Z. S. Du and T. A. Lipo, "Efficient Utilization of Rare Earth Permanent-Magnet Materials and Torque Ripple Reduction in Interior Permanent-Magnet Machines," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 3485-3495, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2017.2687879.
K. Wang, Z. Q. Zhu, G. Ombach, and W. Chlebosz, "Average torque improvement of interior permanent-magnet machine using third harmonic in rotor shape," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 61, no. 9, pp. 5047-5057, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2013.2286085.
A. J. Piña, S. Paul, R. Islam and L. Xu, "Effect of manufacturing variations on cogging torque in surface-mounted permanent magnet motors," 2015 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), pp. 4843-4850, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2015.7310343.
H. Qian, H. Guo, Z. Wu and X. Ding, "Analytical Solution for Cogging Torque in Surface-Mounted Permanent-Magnet Motors with Magnet Imperfections and Rotor Eccentricity," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 50, no. 8, pp. 1-15, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2014.2312179.
L. Gasparin, A. Cernigoj, S. Markic and R. Fiser, "Additional Cogging Torque Components in Permanent-Magnet Motors Due to Manufacturing Imperfections," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 1210-1213, 2009, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2009.2012561.
M. Nakano, Y. Morita and T. Matsunaga, "Reduction of cogging torque due to production tolerances of rotor by using partially placed dummy slots in axial direction," 2014 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), pp. 5579-5586, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1109/ECCE.2014.6954165.
I. Coenen, M. van der Giet and K. Hameyer, "Manufacturing Tolerances: Estimation and Prediction of Cogging Torque Influenced by Magnetization Faults," IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, vol. 48, no. 5, pp. 1932-1936, 2012, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2178252.
X. Ge and Z. Q. Zhu, "Sensitivity of manufacturing tolerances on cogging torque in interior permanent magnet machines with different Slot/Pole number combinations," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 3557-3567, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2017.2693258.
X. Ge and Z. Q. Zhu, "Influence of manufacturing tolerances on cogging torque in interior permanent magnet machines with eccentric and sinusoidal rotor contours," IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, vol. 53, no. 4, pp. 3568-3578, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/TIA.2017.2693264.
Z. Q. Zhu and D. Howe, "Influence of design parameters on cogging torque in permanent magnet machines," in IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 407-412, 2000, https://doi.org/10.1109/60.900501.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Ahlam Luaibi Shuraiji, Kassim Rasheed Hameed, Salam Waley Shneen

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


