Accurate Crowd Counting Using an Enhanced LCDANet with Multi-Scale Attention Modules
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v7i3.14391Keywords:
Crowd Counting, Density Estimation, MicroASPP, Attention Mechanismss, Inference of CrowdAbstract
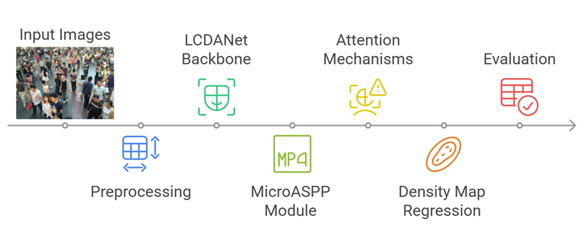
Accurate crowd counting remains a challenging task due to occlusion, scale variation, and complex scene layouts. This study proposes ME-LCDANet, an enhanced deep learning framework built upon the LCDANet backbone, integrating multi-scale feature extraction via Micro Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (MicroASPP) and attention refinement using CBAMLite modules. A preprocessing pipeline with Gaussian-based density maps, synchronized augmentations, and a dual-objective loss function combining density and count supervision supports effective training and generalization. Experimental evaluation on the ShanghaiTech Part B dataset demonstrates a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 11.50 (95% CI: 10.20–12.91) and a Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) of 11.54 (95% CI: 10.26–12.99). Training dynamics indicate steadily declining loss and reduced validation MAE, while gradient norm analysis suggests reliable convergence. Comparative results show that, although CSRNet and SaNet achieve slightly lower MAE, ME-LCDANet attains a notably reduced RMSE, reflecting robustness against large prediction deviations. While the study focuses on a single benchmark dataset, the proposed architecture offers a promising approach for robust crowd counting in diverse scenarios.
References
B. Li, H. Huang, A. Zhang, P. Liu, and C. Liu, "Approaches on crowd counting and density estimation: a review," Pattern Analysis and Applications, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 853–874, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10044-021-00959-z.
M. Wang, X. Zhou, and Y. Chen, "A comprehensive survey of crowd density estimation and counting," IET Image Processing, vol. 19, no. 1, p. e13328, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.13328.
A. Serek, B. Amirgaliyev, R. Y. M. Li, A. Zhumadillayeva and D. Yedilkhan, "Crowd Density Estimation Using Enhanced Multi-Column Convolutional Neural Network and Adaptive Collation," in IEEE Access, vol. 13, pp. 146956-146972, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3597393.
T. Daware and T. Dhote, "Enhancing public safety through real-time crowd density analysis and management," in Proc. 2023 5th Int. Conf. Inventive Res. Comput. Appl. (ICIRCA), pp. 1040–1046, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIRCA57980.2023.10220731.
M. Patidar, P. K. Bhanodia, P. K. Patidar, R. Shukla, K. Gupta, and S. Rajpoot, "Advanced crowd density estimation using hybrid CNN models for real-time public safety applications," Library of Progress – Library Science, Information Technology & Computer, vol. 44, no. 3, 2024, https://openurl.ebsco.com/EPDB%3Agcd%3A4%3A23637460/detailv2?sid=ebsco%3Aplink%3Ascholar&id=ebsco%3Agcd%3A180918700&crl=c&link_origin=scholar.google.com.
Y. Liu, Z. Yu, H. Cui, S. Helal, and B. Guo, "SafeCity: A heterogeneous mobile crowd sensing system for urban public safety," IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 10, no. 20, pp. 18330–18345, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/JIOT.2023.3279385.
R. Jiang, Z. Cai, Z. Wang, C. Yang, Z. Fan, Q. Chen, … and R. Shibasaki, "DeepCrowd: A deep model for large-scale citywide crowd density and flow prediction," IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 276–290, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2021.3077056.
N. K. Saini and R. Sharma, "Deep learning approaches for crowd density estimation: A review," in Proc. 2023 12th Int. Conf. Syst. Modeling & Advancement Res. Trends (SMART), pp. 83–88, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/SMART59791.2023.10428557.
M. H. El-Didy, G. F. Hassan, S. Afifi, and A. Ismail, "Crowding between urban planning and environmental psychology: Guidelines for bridging the gap," Open House International, vol. 49, no. 4, pp. 670–695, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1108/OHI-06-2023-0146.
D. Darsena, G. Gelli, I. Iudice, and F. Verde, "Sensing technologies for crowd management, adaptation, and information dissemination in public transportation systems: A review," IEEE Sensors Journal, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 68–87, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2022.3223297.
Y. Zhu, K. Ni, X. Li, A. Zaman, X. Liu, and Y. Bai, "Artificial intelligence aided crowd analytics in rail transit station," Transp. Res. Rec., vol. 2678, no. 2, pp. 481–492, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1177/03611981231175156 .
W. Tang, K. Liu, M. S. Shakeel, H. Wang, and W. Kang, "DDAD: detachable crowd density estimation assisted pedestrian detection," IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 1867–1878, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2022.3222692.
V. X. Gong, W. Daamen, A. Bozzon, and S. P. Hoogendoorn, "Counting people in the crowd using social media images for crowd management in city events," Transportation, vol. 48, no. 6, pp. 3085–3119, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11116-020-10159-z.
O. Elharrouss, H. H. Mohammed, S. Al-Maadeed, K. Abualsaud, A. Mohamed and T. Khattab, "Crowd density estimation with a block-based density map generation," 2024 International Conference on Intelligent Systems and Computer Vision (ISCV), pp. 1-7, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCV60512.2024.10620151.
X. Zhang, Y. Sun, Q. Li, X. Li, and X. Shi, "Crowd density estimation and mapping method based on surveillance video and GIS," ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf., vol. 12, no. 2, p. 56, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12020056.
M. Chengo, J. Bitok, and S. W. Maingi, "Crowd management, risk assessment strategies and sports tourism events in Nairobi County, Kenya," J. Hospitality Tourism Manage., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 46–66, 2024, https://doi.org/10.53819/81018102t4253.
S. Huang, J. Ji, Y. Wang, W. Li, and Y. Zheng, "A machine vision-based method for crowd density estimation and evacuation simulation," Safety Science, vol. 167, p. 106285, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssci.2023.106285.
A. M. Alasmari, N. S. Farooqi, and Y. A. Alotaibi, "Recent trends in crowd management using deep learning techniques: a systematic literature review," J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Eng. Archit., pp. 1–29, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/s43995-024-00071-3.
T. Zhang, J. Yuan, Y. C. Chen, and W. Jia, "Self-learning soft computing algorithms for prediction machines of estimating crowd density," Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 105, p. 107240, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107240.
M. Fiandeiro, T. T. Nguyen, H. Wong, and E. B. Hsu, "Modernized crowd counting strategies for mass gatherings—A review," J. Acute Med., vol. 13, no. 1, p. 4, 2023, https://doi.org/10.6705/j.jacme.202303_13(1).0002.
S. Goel, D. Koundal, and R. Nijhawan, "Learning models in crowd analysis: A review," Arch. Comput. Methods Eng., vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 943–961, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-024-10151-1.
Y. C. Li, R. S. Jia, Y. X. Hu, and H. M. Sun, "A lightweight dense crowd density estimation network for efficient compression models," Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 238, p. 122069, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2023.122069.
J. P. Singh, M. Kumar, A. Arya, and B. Badmera, "Scientific exploration for density estimation and crowd counting of crowded scene," in J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., vol. 1947, no. 1, p. 012019, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1947/1/012019.
Y. Ranasinghe, N. G. Nair, W. G. C. Bandara, and V. M. Patel, "CrowdDiff: Multi-hypothesis crowd density estimation using diffusion models," in Proc. IEEE/CVF Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), pp. 12809–12819, 204, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52733.2024.01217.
A. A. Assefa, W. Tian, N. W. Hundera, and M. U. Aftab, "Crowd density estimation in spatial and temporal distortion environment using parallel multi-size receptive fields and stack ensemble meta-learning," Symmetry, vol. 14, no. 10, p. 2159, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/sym14102159.
Y. C. Li, R. S. Jia, Y. X. Hu, D. N. Han, and H. M. Sun, "Crowd density estimation based on multi scale features fusion network with reverse attention mechanism," Appl. Intell., vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 13097–13113, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-022-03187-y.
M. Wang, X. Zhou, and Y. Chen, "A comprehensive survey of crowd density estimation and counting," IET Image Process., vol. 19, no. 1, p. e13328, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1049/ipr2.13328.
X. Zhang, Y. Sun, Q. Li, X. Li, and X. Shi, "Crowd density estimation and mapping method based on surveillance video and GIS," ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf., vol. 12, no. 2, p. 56, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi12020056.
R. Gouiaa, M. A. Akhloufi, and M. Shahbazi, "Advances in convolution neural networks based crowd counting and density estimation," Big Data Cogn. Comput., vol. 5, no. 4, p. 50, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/bdcc5040050.
G. Yang and D. Zhu, "Survey on algorithms of people counting in dense crowd and crowd density estimation," Multimedia Tools Appl., vol. 82, no. 9, pp. 13637–13648, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-022-13957-y.
L. Zholshiyeva, T. Zhukabayeba, A. Serek, R. Duisenbek, M. Berdieva, and N. Shapay, “Deep learning-based continuous sign language recognition,” Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC), vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1106–1118, 2025, https://doi.org/10.18196/jrc.v6i1.23879.
X. Zhao, L. Wang, Y. Zhang, X. Han, M. Deveci, and M. Parmar, “A review of convolutional neural networks in computer vision,” Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 57, no. 4, p. 99, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-024-10721-6.
L. Zholshiyeva, T. Zhukabayeva, D. Baumuratova, and A. Serek, “Design of QazSL sign language recognition system for physically impaired individuals,” Journal of Robotics and Control (JRC), vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 191–201, 2025, https://doi.org/10.18196/jrc.v6i1.23879.
M. A. Khan, H. Menouar, and R. Hamila, “Revisiting crowd counting: State-of-the-art, trends, and future perspectives,” Image and Vision Computing, vol. 129, p. 104597, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2022.104597.
L. Dong, H. Zhang, K. Yang, D. Zhou, J. Shi, and J. Ma, “Crowd counting by using top-k relations: A mixed ground-truth CNN framework,” IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, vol. 68, no. 3, pp. 307–316, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/TCE.2022.3190384.
S. Zhang, W. Wang, W. Zhao, L. Wang, and Q. Li, “A cross-modal crowd counting method combining CNN and cross-modal transformer,” Image and Vision Computing, vol. 129, p. 104592, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2022.104592.
P. Purwono, A. Ma’arif, W. Rahmaniar, H. I. K. Fathurrahman, A. Z. K. Frisky, and Q. M. ul Haq, “Understanding of convolutional neural network (CNN): A review,” International Journal of Robotics and Control Systems, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 739–748, 2022, https://doi.org/10.31763/ijrcs.v2i4.888.
D. Bhatt, C. Patel, H. Talsania, J. Patel, R. Vaghela, S. Pandya, et al., “CNN variants for computer vision: History, architecture, application, challenges and future scope,” Electronics, vol. 10, no. 20, p. 2470, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202470.
L. Alzubaidi, J. Zhang, A. J. Humaidi, A. Al-Dujaili, Y. Duan, O. Al-Shamma, et al., “Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions,” Journal of Big Data, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 53, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-021-00444-8.
J. Gupta, S. Pathak, and G. Kumar, “Deep learning (CNN) and transfer learning: A review,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 2273, no. 1, p. 012029, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2273/1/012029.
J. Lu, L. Tan, and H. Jiang, “Review on convolutional neural network (CNN) applied to plant leaf disease classification,” Agriculture, vol. 11, no. 8, p. 707, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture11080707.
A. W. Salehi, S. Khan, G. Gupta, B. I. Alabduallah, A. Almjally, H. Alsolai, et al., “A study of CNN and transfer learning in medical imaging: Advantages, challenges, future scope,” Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 7, p. 5930, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075930.
L. Deng, Q. Zhou, S. Wang, J. M. Górriz, and Y. Zhang, “Deep learning in crowd counting: A survey,” CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 1043–1077, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1049/cit2.12241.
J. Zhang, S. Chen, S. Tian, W. Gong, G. Cai, and Y. Wang, “A crowd counting framework combining with crowd location,” Journal of Advanced Transportation, vol. 2021, no. 1, p. 6664281, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6664281.
D. Baktibayev, A. Serek, B. Berlikozha, and B. Rustauletov, “Resource-efficient sentiment classification of app reviews using a CNN-BiLSTM hybrid model,” Buletin Ilmiah Sarjana Teknik Elektro, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 427–433, 2025, https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v7i3.13954.
A. Shabir, K. T. Ahmed, K. Kanwal, A. Almas, S. Raza, M. Fatima, and T. Abbas, “A systematic review of attention models in natural language processing,” Statistics, Computing and Interdisciplinary Research, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 33–56, 2024, https://doi.org/10.52700/scir.v6i1.157.
A. de Santana Correia and E. L. Colombini, “Attention, please! A survey of neural attention models in deep learning,” Artificial Intelligence Review, vol. 55, no. 8, pp. 6037–6124, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10462-022-10148-x.
N. Zhang and J. Kim, “A survey on attention mechanism in NLP,” in Proc. 2023 Int. Conf. Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), pp. 1–4, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEIC57457.2023.10049971.
T. Wang, T. Zhang, K. Zhang, H. Wang, M. Li, and J. Lu, “Context attention fusion network for crowd counting,” Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 271, p. 110541, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2023.110541.
B. Tyagi, S. Nigam, and R. Singh, “A review of deep learning techniques for crowd behavior analysis,” Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, vol. 29, no. 7, pp. 5427–5455, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-022-09772-1.
A. Tomar, S. Kumar, and B. Pant, “Crowd analysis in video surveillance: A review,” in Proc. 2022 Int. Conf. Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), pp. 162–168, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/DASA54658.2022.9765008.
Z. Fan, H. Zhang, Z. Zhang, G. Lu, Y. Zhang, and Y. Wang, “A survey of crowd counting and density estimation based on convolutional neural network,” Neurocomputing, vol. 472, pp. 224–251, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2021.02.103.
U. Singh, J. F. Determe, F. Horlin, and P. De Doncker, “Crowd monitoring: State-of-the-art and future directions,” IETE Technical Review, vol. 38, no. 6, pp. 578–594, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2020.1803152.
F. Wang, K. Liu, F. Long, N. Sang, X. Xia, and J. Sang, “Joint CNN and transformer network via weakly supervised learning for efficient crowd counting,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.06388, 2022, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2203.06388.
M. A. Khan, H. Menouar, and R. Hamila, “LCDnet: A Lightweight Crowd Density Estimation Model for Real-time Video Surveillance,” arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.05374, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-023-01286-8.
Z. Yan, P. Li, B. Wang, D. Ren, and W. Zuo, “Towards learning multi-domain crowd counting,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 33, no. 11, pp. 6544–6557, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3137593.
K. B. A. Hassen, J. J. Machado, and J. M. R. Tavares, “Convolutional neural networks and heuristic methods for crowd counting: A systematic review,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 14, p. 5286, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/s22145286.
M. J. Babar, M. Husnain, M. M. S. Missen, A. Samad, M. Nasir, and A. K. N. Khan, “Crowd counting and density estimation using deep network—a comprehensive survey,” Authorea Preprints, 2023, https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.23256587.
Y. Hao, H. Du, M. Mao, Y. Liu, and J. Fan, “A survey on regression-based crowd counting techniques,” Information Technology and Control, vol. 52, no. 3, pp. 693–712, 2023, https://doi.org/10.5755/j01.itc.52.3.33701.
Y. Zhang, D. Zhou, S. Chen, S. Gao, and Y. Ma, “Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 589–597, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.70.
Y. Li, X. Zhang, and D. Chen, “CSRNet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 1091–1100, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00120.
S. Chaudhari, V. Mithal, G. Polatkan, and R. Ramanath, “An attentive survey of attention models,” ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST), vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 1–32, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1145/3465055.
X. Cao, Z. Wang, Y. Zhao, and F. Su, “Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting,” in Proc. Eur. Conf. Computer Vision (ECCV), pp. 734–750, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01228-1_45.
Y. Li, J. Luo, X. Kong, Y. Liu, D. Fei, Y. Wang, et al., “A method for regional crowd flow prediction based on crowd number estimation network,” in Proc. 2024 7th Int. Conf. Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing (MLNLP), pp. 1–5, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1109/MLNLP63328.2024.10800344.
H. Lee and J. Lee, “TinyCount: an efficient crowd counting network for intelligent surveillance,” J. Real-Time Image Process., vol. 21, no. 4, p. 153, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-024-01531-8.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nurmukhammed Abeuov, Daniyar Absatov, Yelnur Mutaliyev, Azamat Serek

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


