Comparison of Machine Learning Algorithms with Feature Engineering for Epileptic Seizure Prediction Based on Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v7i4.13145Keywords:
Epilepsy, EEG, Seizure Prediction, Machine Learning, Feature ExtractionAbstract
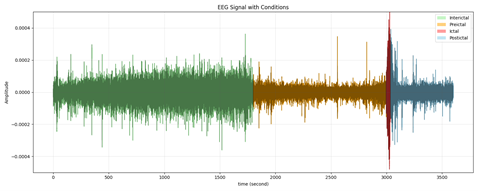
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder marked by recurrent seizures, which can greatly reduce patients' quality of life. Early and accurate seizure prediction is essential for effective clinical intervention and patient safety. This study proposes and evaluates a seizure prediction system using EEG signals processed through machine learning techniques combined with optimized feature extraction methods. The research contribution is the comprehensive comparative analysis of classifier-feature pairs for identifying the most effective configuration for seizure prediction tasks. Three classifiers—Random Forest (RF), Support Vector Machine (SVM), and Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost)—were systematically compared, each combined with precisely engineered feature extraction methods, including Common Spatial Pattern (CSP), Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT), statistical features, and frequency domain features. EEG data from seven patients, totaling approximately 68 hours with 40 seizure events, were obtained from the Children's Hospital Boston database. The results demonstrate that XGBoost with CSP features achieved the highest overall accuracy at 88% and specificity at 88%, while XGBoost with DWT features reached the highest sensitivity at 87%. Additional metrics including F1-score (0.85) and AUC-ROC (0.91) confirmed XGBoost's superior performance. Comparison with five recent studies showed our approach offers a 3-5% improvement in accuracy and sensitivity. These findings highlight the critical impact of both classifier selection and feature engineering in improving EEG-based seizure prediction, with implications for developing real-time monitoring systems despite challenges in clinical implementation due to inter-patient variability.
References
World Health Organization, "Epilepsy," WHO Fact Sheet, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy.
J. W. Sander, "The epidemiology of epilepsy revisited," Current Opinion in Neurology, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 165-170, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wco.0000063766.15877.8e.
A. Jacoby et al., ”Stigma and epilepsy: A review of the literature,” Epilepsy Behav, vol 12, no. 4, pp. 540-546, 2008, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-008-0052-8.
S. G. Sheth, G. Krauss, A. Krumholz, and G. Li, “Mortality in epilepsy: driving fatalities vs other causes of death in patients with epilepsy,” Neurology, vol 63, no. 6, p. 1002-1007, 2004, https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000138590.00074.9a.
R. S. Fisher et al., "ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy," Epilepsia, vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 475-482, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12550.
F. Mormann et al., “On the predictability of epileptic seizures,” Clinical Neurophysiology, vol. 116, no. 3, pp. 569-587, 2005, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2004.08.025.
E. Niedermeyer and F. L. da Silva. Electroencephalography: basic principles, clinical applications, and related fields. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2005, https://books.google.co.id/books?hl=id&lr=&id=tndqYGPHQdEC.
U. R. Acharya et al., “Deep convolutional neural network for the automated detection and diagnosis of seizure using EEG signals,” Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol. 100, pp. 270-278, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2017.09.017.
A. Shoeb et al., "Patient-specific seizure onset detection," Epilepsy & Behavior, vol. 5, no. 4, pp 483-498, 2004, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2004.05.005.
L. Kuhlmann et al., “Epilepsyecosystem.org: crowd-sourcing reproducible seizure prediction with long-term human intracranial EEG,” Brain, vol. 141, no. 9, pp. 2619–2630, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy210.
J. Wu, T. Zhou, and T. Li, "Detecting epileptic seizures in EEG signals with complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition and extreme gradient boosting," Entropy, vol. 22, no. 2, p. 140, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020140.
M. Zho et al, “Epileptic Seizure Detection Based on EEG Signals and CNN,” Front. Neuroinform, vol. 12, p. 95, 2018, https://doi.org/10.3389/fninf.2018.00095.
Y. M. Dweiri and T. K. Al-Omary, "Novel ML-based algorithm for detecting seizures from single-channel EEG," NeuroSci, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 59-70, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci5010004.
B. Richhariya, M. Tanveer, “EEG signal classification using universum support vector machine,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 106, pp. 169-182, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2018.03.053.
W. Chen et al., “A random forest model based classification scheme for neonatal amplitude-integrated EEG,” BioMed Eng OnLine, vol. 13 (Suppl 2), 2014, https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-925X-13-S2-S4.
F. Wang, et al, “An ensemble of Xgboost models for detecting disorders of consciousness in brain injuries through EEG connectivity,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 198, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116778.
A. Subasi, M. Ismail Gursoy, "EEG signal classification using PCA, ICA, LDA and support vector machines,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 37, 12, pp. 8659-8666, 2010, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2010.06.065.
K. M. Tsiouris et al., "A Long Short-Term Memory deep learning network for the prediction of epileptic seizures using EEG signals," Computers in Biology and Medicine, vol. 99, pp. 24-37, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.05.019.
R. Ben Messaoud and M. Chavez, "Random Forest classifier for EEG-based seizure prediction," arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.04510, 2021, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2106.04510.
C. L. Liu et al, "Epileptic Seizure Prediction With Multi-View Convolutional Neural Networks," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 170352-170361, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2955285.
X. Wang, G. Gong, and N. Li, "Detection analysis of epileptic EEG using a novel random forest model combined with grid search optimization," Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, vol. 13, p. 52, 2019, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2019.00052.
A. Goldberger et al., "PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals," Circulation, vol. 101, no. 23, pp. e215-e220, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.101.23.e215.
J. R. Williamson et al., “Seizure prediction using EEG spatiotemporal correlation structure,” Epilepsy & Behavior, vol. 25, 2, pp. 230-238, 2012, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.07.007.
S. Ibrahim, R. Djemal, and A. Alsuwailem, "Electroencephalography (EEG) signal processing for epilepsy and autism spectrum disorder diagnosis," Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, vol. 38, no. 1, pp. 16-26, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2017.08.006.
S. Ibrahim, R. Djemal, A. Alsuwailem, and S. Gannouni, "Electroencephalography (EEG)-based epileptic seizure prediction using entropy and K-nearest neighbor (KNN)," Communications in Science and Technology, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 23-30, 2022, https://doi.org/10.21924/cst.2.1.2017.44.
R. S. Fisher et al., "Instruction manual for the ILAE 2017 operational classification of seizure types," Epilepsia, vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 531-542, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13671.
N. V. Chawla et al., "SMOTE: Synthetic minority over-sampling technique," Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research, vol. 16, pp. 321-357, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1613/jair.953.
P. Boonyakitanont, A. Lek-uthai, K. Chomtho, and J. Songsiri, "A review of feature extraction and performance evaluation in epileptic seizure detection using EEG," Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, vol. 57, p. 101702, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101702.
N. F. Fumeaux et al., “Accurate detection of spontaneous seizures using a generalized linear model with external validation,” Epilepsia, vol. 61, no. 9, pp. 1906-1918, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.16628.
N. D. Truong et al., "Convolutional neural networks for seizure prediction using intracranial and scalp electroencephalogram,” Neural Networks, vol. 105, pp. 104-111, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.018.
M. Aljalal, S. A. Aldosari, K. Alsharabi, A. M. Abdurraqeeb, and F. A. Alturki, "Parkinson's disease detection from resting-state EEG signals using common spatial pattern, entropy, and machine learning techniques," Diagnostics, vol. 12, no. 5, p. 1033, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051033.
X. Wang, C. Li, R. Zhang, L. Wang, J. Tan, and H. Wang, "Intelligent extraction of salient feature from electroencephalogram using redundant discrete wavelet transform," Frontiers in Neuroscience, vol. 16, p. 921642, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.921642.
R. Akut, “Wavelet based deep learning approach for epilepsy detection,” Health Inf Sci Syst, vol. 7, no. 1, p. 8, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13755-019-0069-1.
Y. Lei and Z. Wu, "Time series classification based on statistical features," EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, vol. 2020, no. 1, pp. 1-9, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-020-1661-4.
F. Lotte et al., "A review of classification algorithms for EEG-based brain–computer interfaces: a 10 year update," Journal of Neural Engineering, vol. 15, no. 3, p. 031005, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1088/1741-2552/aab2f2.
Q. Feng, J. Liu, and J. Gong, "UAV Remote sensing for urban vegetation mapping using random forest and texture analysis," Remote Sensing, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1094-1115, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70101074.
M. J. Antony et al., “Classification of EEG Using Adaptive SVM Classifier with CSP and Online Recursive Independent Component Analysis,” Sensors (Basel), vol. 22, no. 19, p. 7596, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/s22197596.
T. Chen and C. Guestrin, "XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system," Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, pp. 785-794, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1145/2939672.2939785.
S. Kumar, A. Sharma, & T. Tsunoda, “An improved discriminative filter bank selection approach for motor imagery EEG signal classification using mutual information,” BMC Bioinformatics, vol. 18 (Suppl 16), p. 545, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-017-1964-6.
D. Khurshid et al., “A deep neural network-based approach for seizure activity recognition of epilepsy sufferers,” Front Med (Lausanne), vol. 11, p. 1405848, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2024.1405848.
K. Veena, K. Meena, Y. Teekaraman, R. Kuppusamy, and A. Radhakrishnan, "C SVM Classification and KNN Techniques for Cyber Crime Detection," Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, vol. 2022, p. 3640017, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/3640017.
Y. Yuan, G. Xun, K. Jia, and A. Zhang, "A multi-view deep learning framework for EEG seizure detection," IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 83-94, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/jbhi.2018.2871678.
T. Wen and Z. Zhang, "Deep Convolution Neural Network and Autoencoders-Based Unsupervised Feature Learning of EEG Signals," in IEEE Access, vol. 6, pp. 25399-25410, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2833746.
X. Yin, M. Meng, Q. She, Y. Gao, and Z. Luo, "Optimal channel-based sparse time-frequency blocks common spatial pattern feature extraction method for motor imagery classification," Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 3421-3438, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3934/mbe.2021213.
A. T. Tzallas, M. G. Tsipouras and D. I. Fotiadis, "Epileptic Seizure Detection in EEGs Using Time–Frequency Analysis," in IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 703-710, 2009, https://doi.org/10.1109/TITB.2009.2017939.
M. Sharma et al., “An automatic detection of focal EEG signals using new class of time–frequency localized orthogonal wavelet filter banks,” Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 118, pp. 217-227, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2016.11.024.
N. Rafiuddin, Y. U. Khan and O. Farooq, "Feature extraction and classification of EEG for automatic seizure detection," 2011 International Conference on Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies, pp. 184-187, 2011, https://doi.org/10.1109/MSPCT.2011.6150470.
A. Subasi, J. Kevric, and M. Abdullah Canbaz, “Epileptic seizure detection using hybrid machine learning methods,” Neural Comput & Applic, vol. 31, pp. 317–325, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3003-y.
A. Gramacki, A., and J. Gramacki, “A deep learning framework for epileptic seizure detection based on neonatal EEG signals,” Sci Rep, vol. 12, p. 13010, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-15830-2.
Y. Zhang, C. S. Nam, G. Zhou, J. Jin, X. Wang and A. Cichocki, "Temporally Constrained Sparse Group Spatial Patterns for Motor Imagery BCI," in IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 49, no. 9, pp. 3322-3332, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2018.2841847.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sutrisno Ibrahim, Faisal Rahutomo, Reihan Henda, Majid Aljalal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


