An Innovation Approach for Feature Selection Medical Data Using Joint Fine-Tuning Fusion Graph Convolutional Network
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v7i4.11652Keywords:
Feature Selection, Graph Convolutional Networks, Medical Data, Joint Fine-Tuning, Clinical Decision SupportAbstract
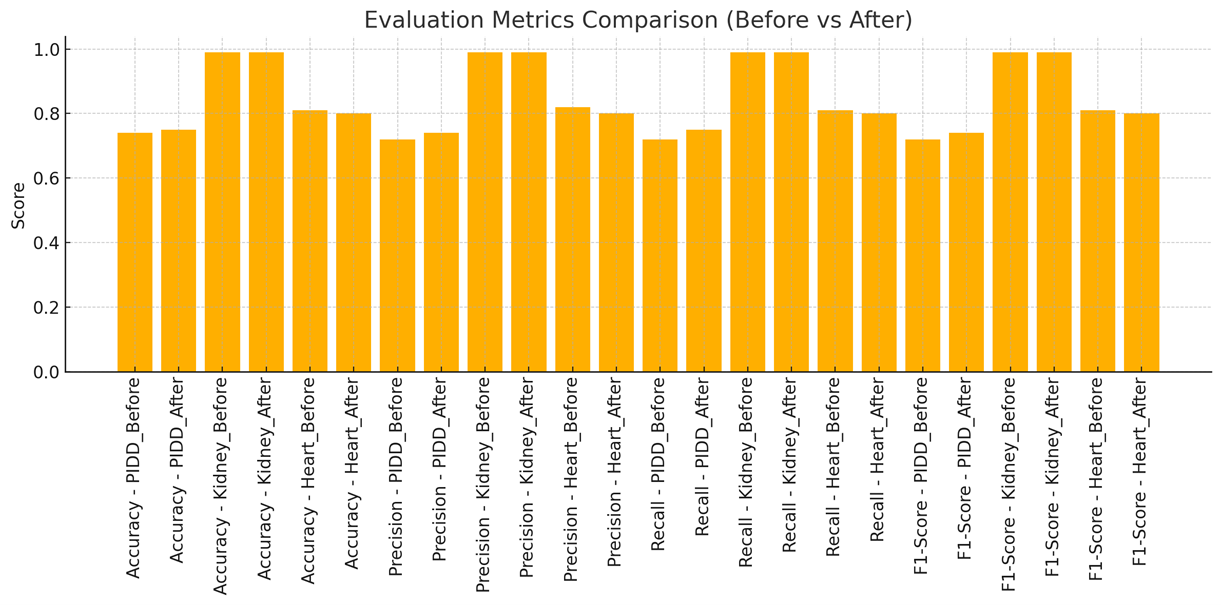
This research addresses the challenge of feature selection in high dimensional medical datasets, where unnecessary or duplicated information can hide patterns and negatively impact model performance. The aim is to develop an efficient feature selection strategy using Fine-tuning Fusion Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) to enhance model accuracy and interpretability. The objectives include improving the medical data selection process, increasing generalization, and assisting healthcare professionals in making educated clinical decisions based on the most relevant factors. The study employs Joint Fine-Tuning Fusion Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) for feature selection in medical datasets. This approach entails creating several graphs to illustrate feature interrelations, amalgamating them into a cohesive representation, and optimizing the model to emphasize pertinent aspects. The L2-norm of the final embeddings dictates feature significance, directing the choice of the most critical features for enhanced predictive accuracy. The study's findings indicate that GCN-based feature selection improves classification accuracy, especially for the PIDD dataset, enhancing accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score from 0.74 to 0.75. The Kidney Failure dataset exhibited near-perfect accuracy (0.99) prior to selection, whereas the heart disease dataset had a minor reduction in performance (from 0.81 to 0.80), highlighting the dataset-specific effects of feature selection. GCN-based feature selection improved classification performance, increasing the PIDD dataset's accuracy from 0.74 to 0.75, with no significant effect on the Kidney Failure dataset. Nonetheless, it somewhat diminished performance for the heart disease dataset. Subsequent study ought to enhance feature selection techniques by integrating dataset-specific optimizations and domain expertise to augment model precision and overall generalizability.
References
C. M. Cutillo et al., “Machine intelligence in healthcare—perspectives on trustworthiness, explainability, usability, and transparency,” Npj Digit. Med., vol. 3, no. 1, p. 47, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-020-0254-2.
E. Y. Boateng and D. A. Abaye, “A Review of the Logistic Regression Model with Emphasis on Medical Research,” J. Data Anal. Inf. Process., vol. 07, no. 04, pp. 190–207, 2019, https://doi.org/10.4236/jdaip.2019.74012.
A. Alzubaidi, “Challenges in Developing Prediction Models for Multi-modal High-Throughput Biomedical Data,” in Intelligent Systems and Applications, vol. 868, 1056–1069, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01054-6_73.
B. Çil, H. Ayyıldız, and T. Tuncer, “Discrimination of β-thalassemia and iron deficiency anemia through extreme learning machine and regularized extreme learning machine based decision support system,” Med. Hypotheses, vol. 138, p. 109611, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109611.
[5] D. C. E. Saputra, K. Sunat, and T. Ratnaningsih, “A new artificial intelligence approach using extreme learning machine as the potentially effective model to predict and analyze the diagnosis of anemia,” Healthcare, vol. 11, no. 5, p. 697, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11050697.
D. C. E. Saputra, Y. Maulana, E. Faristasari, A. Ma’arif, and I. Suwarno, “Machine Learning Performance Analysis for Classification of Medical Specialties,” in Proceeding of the 3rd International Conference on Electronics, Biomedical Engineering, and Health Informatics, vol. 1008, pp. 513–528, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0248-4_34.
C. Guo and J. Chen, “Big Data Analytics in Healthcare,” in Knowledge Technology and Systems, vol. 34, pp. 27–70, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1075-5_2.
M. M. Chowdhury, R. S. Ayon, and M. S. Hossain, “An investigation of machine learning algorithms and data augmentation techniques for diabetes diagnosis using class imbalanced BRFSS dataset,” Healthc. Anal., vol. 5, p. 100297, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.health.2023.100297.
M. Ağraz, E. Eğrioğlu, E. Baş, M.-Y. Chen, D. Göksülük, and M. F. Burak, “Diabetes Development Prediction Using a Hybrid Model Combining Dendritic Artificial Neuron Model and Logistic Regression,” Endocrinol. Res. Pract., vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 84–93, 2025, https://doi.org/10.5152/erp.2025.24585.
C. Prod’homme et al., “Can palliative care consultation increase integration of palliative care for patients with hematologic malignancies?,” Blood Adv., vol. 5, no. 8, pp. 2123–2127, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004369.
P. Martens, P. Nijst, F. H. Verbrugge, K. Smeets, M. Dupont, and W. Mullens, “Impact of iron deficiency on exercise capacity and outcome in heart failure with reduced, mid-range and preserved ejection fraction,” Acta Cardiol., vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 115–123, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1080/00015385.2017.1351239.
P. Y. Taser, “Application of Bagging and Boosting Approaches Using Decision Tree-Based Algorithms in Diabetes Risk Prediction,” in The 7th International Management Information Systems Conference, p. 6, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/proceedings2021074006.
M. Kashina, I. D. Lenivtceva, and G. D. Kopanitsa, “Preprocessing of unstructured medical data: the impact of each preprocessing stage on classification,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 178, pp. 284–290, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2020.11.030.
D. C. E. Saputra, E. I. Muryadi, R. Phann, I. Futri, and L. Lismawati, “An Innovative Artificial Intelligence-Based Extreme Learning Machine Based on Random Forest Classifier for Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus,” J. Ilm. Tek. Elektro Komput. Dan Inform., vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 173–187, 2024, https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v10i1.28690.
D. C. E. Saputra, Y. Maulana, T. A. Win, R. Phann, and W. Caesarendra, “Implementation of Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models Based on Structural MRI for Identification of Autism Spectrum Disorder,” vol. 9, no. 2, 2023, https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v9i2.26094.
Z. Cai, H. Huang, G. Sun, ZiQiang. Li, and ChengJu. Ouyang, “Advancing Predictive Models: Unveiling LightGBM Machine Learning for Data Analysis,” in 2023 4th International Conference on Computer, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (ICCBD+AI), pp. 109–112, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/iccbd-ai62252.2023.00027.
V. R. S. Kushwah and K. Verma, “Security and Privacy Challenges for Big Data on Social Media,” in Big Data Analytics in Cognitive Social Media and Literary Texts, pp. 267–285, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-4729-1_15.
U. Jain, S. Kumar, S. Dubey, O. Sharma, and V. Kumar Jain, “Virtualization-A New Dimension of Big Data,” in 2018 8th International Conference on Cloud Computing, Data Science & Engineering (Confluence), pp. 803–808, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1109/CONFLUENCE.2018.8443075.
D. Albashish, A. I. Hammouri, M. Braik, J. Atwan, and S. Sahran, “Binary biogeography-based optimization based SVM-RFE for feature selection,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 101, p. 107026, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.107026.
S. Sivaranjani, S. Ananya, J. Aravinth, and R. Karthika, “Diabetes Prediction using Machine Learning Algorithms with Feature Selection and Dimensionality Reduction,” in 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), pp. 141–146, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS51430.2021.9441935.
Y. Aggarwal, J. Das, P. M. Mazumder, R. Kumar, and R. K. Sinha, “Heart rate variability features from nonlinear cardiac dynamics in identification of diabetes using artificial neural network and support vector machine,” Biocybern. Biomed. Eng., vol. 40, no. 3, pp. 1002–1009, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbe.2020.05.001.
J. V. N. Ramesh, A. Kushwaha, T. Sharma, A. Aranganathan, A. Gupta, and S. K. Jain, “Intelligent Feature Engineering and Feature Selection Techniques for Machine Learning Evaluation,” in Mobile Radio Communications and 5G Networks, vol. 915, pp. 753–764, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-0700-3_56.
M. Y. M. Parvees and M. Raja, “Optimal Feature Subset Selection with Multi-Kernel Extreme Learning Machine for Medical Data Classification,” Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ., vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 3612–3623, 2021, https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.17762/turcomat.v12i6.7157.
S. Li, X. Huang, and D. Wang, “Stochastic configuration networks for multi-dimensional integral evaluation,” Inf. Sci., vol. 601, pp. 323–339, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2022.04.005.
S. Asghari, H. Nematzadeh, E. Akbari, and H. Motameni, “Mutual information-based filter hybrid feature selection method for medical datasets using feature clustering,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 82, no. 27, pp. 42617–42639, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15143-0.
I. Hussain, M. Qureshi, M. Ismail, H. Iftikhar, J. Zywiołek, and J. L. López-Gonzales, “Optimal features selection in the high dimensional data based on robust technique: Application to different health database,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 17, p. e37241, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37241.
G. Sun, C. Jiang, X. Wang, and X. Yang, “Short-term building load forecast based on a data-mining feature selection and LSTM-RNN method,” IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng., vol. 15, no. 7, pp. 1002–1010, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/tee.23144.
T. A. Al-Qablan, M. H. Mohd Noor, M. A. Al-Betar, and A. T. Khader, “Improved gray wolf harris hawk algorithm based feature selection for sentiment analysis,” Results Control Optim., vol. 20, p. 100604, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rico.2025.100604.
A. Bilal, G. Sun, S. Mazhar, and A. Imran, “Improved Grey Wolf Optimization-Based Feature Selection and Classification Using CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection,” in Evolutionary Computing and Mobile Sustainable Networks, vol. 116, pp. 1–14, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9605-3_1.
H. Liu, M. Zhou, and Q. Liu, “An embedded feature selection method for imbalanced data classification,” IEEECAA J. Autom. Sin., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 703–715, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/JAS.2019.1911447.
A. Helisa, T. H. Saragih, I. Budiman, F. Indriani, and D. Kartini, “Prediction of Post-Operative Survival Expectancy in Thoracic Lung Cancer Surgery Using Extreme Learning Machine and SMOTE,” J. Ilm. Tek. Elektro Komput. Dan Inform., vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 239–249, 2023, https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v9i2.25973.
H. Li, X. Shi, X. Zhu, S. Wang, and Z. Zhang, “FSNet: Dual Interpretable Graph Convolutional Network for Alzheimer’s Disease Analysis,” IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 15–25, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/TETCI.2022.3183679.
Y. Liu, H. Zhou, M. Guan, F. Feng, and J. Duan, “Scalp EEG-Based Automatic Detection of Epileptiform Events via Graph Convolutional Network and Bi-Directional LSTM Co-Embedded Broad Learning System,” IEEE Signal Process. Lett., vol. 30, pp. 448–452, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2023.3263433.
R. Hu, Z. Deng, and X. Zhu, “Multi-scale Graph Fusion for Co-saliency Detection.” Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 7789–7796, May 2021, https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i9.16951.
J. Chen, B. Li, and K. He, “Neighborhood convolutional graph neural network,” Knowl.-Based Syst., vol. 295, p. 111861, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2024.111861.
V. Purna Chandra Reddy and K. K. Gurrala, “OHGCNet: Optimal feature selection-based hybrid graph convolutional network model for joint DR-DME classification,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 78, p. 103952, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2022.103952.
Z. Xu, D. Yu, H. Hou, W. Zhang, and Y. Zhang, “Research on Fault Diagnosis of Rolling Bearing in Printing Press Based on Convolutional Neural Network,” in Advances in Graphic Communication, Printing and Packaging Technology and Materials, vol. 754, pp. 487–494, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-0503-1_71.
J. Zheng, Z. Gao, J. Ma, J. Shen, and K. Zhang, “Deep Graph Convolutional Networks for Accurate Automatic Road Network Selection,” ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf., vol. 10, no. 11, p. 768, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10110768.
H. Sadr et al., “Unveiling the potential of artificial intelligence in revolutionizing disease diagnosis and prediction: a comprehensive review of machine learning and deep learning approaches,” Eur. J. Med. Res., vol. 30, no. 1, p. 418, May 2025, https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-025-02680-7.
M. Javaid, A. Haleem, and R. P. Singh, “Health informatics to enhance the healthcare industry’s culture: An extensive analysis of its features, contributions, applications and limitations,” Inform. Health, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 123–148, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoh.2024.05.001.
J. M. Schwartz et al., “Factors Influencing Clinician Trust in Predictive Clinical Decision Support Systems for In-Hospital Deterioration: Qualitative Descriptive Study,” JMIR Hum. Factors, vol. 9, no. 2, p. e33960, 2022, https://doi.org/10.2196/33960.
M. Ennab and H. Mcheick, “Enhancing interpretability and accuracy of AI models in healthcare: a comprehensive review on challenges and future directions,” Front. Robot. AI, vol. 11, p. 1444763, 2024, https://doi.org/10.3389/frobt.2024.1444763.
M. I. Mazdadi, T. H. Saragih, I. Budiman, A. Farmadi, and A. Tajali, “The Effectiveness of Data Imputations on Myocardial Infarction Complication Classification Using Machine Learning Approach with Hyperparameter Tuning,” J. Ilm. Tek. Elektro Komput. Dan Inform., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 520–533, 2024, https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v10i3.29479.
G. Lyu, “Data-driven decision making in patient management: a systematic review,” BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak., vol. 25, no. 1, p. 239, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-025-03072-x.
R. Hu, Z. Deng, and X. Zhu, “Multi-scale graph fusion for co-saliency detection,” AAAI, vol. 35, no. 9, pp. 7789–7796, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1609/aaai.v35i9.16951.
B. E. Dejene, T. M. Abuhay, and D. S. Bogale, “Predicting the level of anemia among Ethiopian pregnant women using homogeneous ensemble machine learning algorithm,” BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak., vol. 22, no. 1, p. 247, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-022-01992-6.
S. Abraham and S. Joseph, “Medical Imaging and Artificial Intelligence: Transforming the Nature of Diagnostics and Treatment,” in Advances in Medical Technologies and Clinical Practice, pp. 127–158, 2024, https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3693-8990-4.ch006.
S. Kukreti, A. Shrivastava, R. Chandrashekar, K. P. Rani, A. Badhoutiya, and S. Lakhanpal, “AI-Driven Clinical Decision Support Systems: Revolutionizing Healthcare With Predictive Models,” in 2025 International Conference on Computational, Communication and Information Technology (ICCCIT), pp. 560–565, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCIT62592.2025.10927929.
Y. Yang, Y. Rao, M. Yu, and Y. Kang, “Multi-layer information fusion based on graph convolutional network for knowledge-driven herb recommendation,” Neural Netw., vol. 146, pp. 1–10, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.11.010.
H. Lin, K. Chen, Y. Xue, S. Zhong, L. Chen, and M. Ye, “Coronary heart disease prediction method fusing domain-adaptive transfer learning with graph convolutional networks (GCN),” Sci. Rep., vol. 13, no. 1, p. 14276, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-33124-z.
Y. Huang and A. C. S. Chung, “Disease prediction with edge-variational graph convolutional networks,” Med. Image Anal., vol. 77, p. 102375, Apr. 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102375.
W. Hou, C. Lin, L. Yu, J. Qin, R. Yu, and L. Wang, “Hybrid Graph Convolutional Network With Online Masked Autoencoder for Robust Multimodal Cancer Survival Prediction,” IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, vol. 42, no. 8, pp. 2462–2473, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2023.3253760.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dimas Chaerul Ekty Saputra, Irianna Futri, Elvaro Islami Muryadi

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


