Agri-food distribution optimization using modified simulated annealing algorithm considering stochastic market demand
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/ijio.v6i1.9406Keywords:
Fresh agricultural product, Modified simulated annealing algorithm, Avocado supply chain, Stochastic demandAbstract
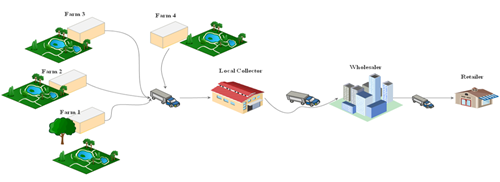
In recent years, the total loss of agricultural fresh product distribution has increased from 20% to 60% of the total amount of harvested products due to their fixed shelf-life time. Consequently, it is essential to select a logistics distribution path that is reasonable for the transportation of fresh agricultural products. To minimize the loss in the distribution of agricultural products in logistics, this study developed an optimization model for agri-food logistic distribution that takes into account the uncertainty of market demand. A novel algorithm called modified simulated annealing (mSA) is introduced to solve a problem with multiple objectives that involves randomness. As a result, the proposed mSA successfully optimizes the availability of the right quantity, quality, and supply chain net profit. The effectiveness of the proposed solution methods is assessed by comparing them with the current state-of-the-art techniques. The findings confirm the effectiveness of the proposed mSA algorithm in tackling the problem across various dimensions. The mSA algorithm led to a decrease in the overall cost of distribution, surpassing the results achieved by SA algorithms. Additionally, the data gathered from the avocado distribution network in the Ethiopian market was used to test the validity of the suggested model. The results showed that as transportation time increased, the quality deterioration rate also increased.
References
C. F. Hsueh and M. S. Chang, "A model for intelligent transportation of perishable products," International Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems Research, vol. 8, pp. 36-41, 2010, doi: 10.1007/s13177-009-0004-y.
H. Van Landeghem and H. Vanmaele, "Robust planning: A new paradigm for demand chain planning," Journal of Operations Management, vol. 20, pp. 769-783, 2002, doi: 10.1016/S0272-6963(02)00039-6.
A. Dwivedi, A. Jha, D. Prajapati, N. Sreenu, and S. Pratap, "Meta-heuristic algorithms for solving the sustainable agro-food grain supply chain network design problem," Modern Supply Chain Research and Applications, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 161-177, 2020, doi: 10.1108/MSCRA-04-2020-0007.
L. Koop, N. M. D. V. Ramos, A. Bonilla-Petriciolet, M. L. Corazza, and F. A. P. Voll, "A review of stochastic optimization algorithms applied in food engineering," International Journal of Chemical Engineering, vol. 2024, no. 1, p. 3636305, 2024, doi: 10.1155/2024/3636305.
M. Christopher, Logistics & Supply Chain Management, Pearson UK, 2016.
B. A. Urra-Calfuñir, C. A. Monardes-Concha, and P. A. Miranda-González, "Agri-food supply chain optimization through a decentralized production process in the olive oil industry," Computers & Industrial Engineering, vol. 192, p. 110185, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2024.110185.
M. Cho, M. Fan, and Y. P. Zhou, "Strategic consumer response to dynamic pricing of perishable products," Consumer-Driven Demand and Operations Management Models, vol. 131, pp. 435-458, 2009, doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-98026-3_17.
J. Lee and I. Moon, "Supplier selection and order allocation problems considering regional and supplier disruptions with a risk-averse strategy," Computers & Industrial Engineering, vol. 187, p. 109810, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2023.109810.
M. Boehlje, "Structural changes in the agricultural industries: How do we measure, analyze and understand them?" American Journal of Agricultural Economics, vol. 81, pp. 1028-1041, 1999, doi: 10.2307/1244080.
O. Ahumada and J. R. Villalobos, "Application of planning models in the agri-food supply chain: A review," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 196, pp. 1-20, 2009, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2008.02.014.
A. Baghalian, S. Rezapour, and R. Z. Farahani, "Robust supply chain network design with service level against disruptions and demand uncertainties: A real-life case," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 227, pp. 199-215, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2012.12.017.
V. Salin, "Information technology in agri-food supply chains," The International Food and Agribusiness Management Review, vol. 1, pp. 329-334, 1998, doi: 10.1016/S1096-7508(99)80003-2.
J. E. Gómez-Lagos, M. C. González-Araya, L. G. Acosta-Espejo, and W. E. Soto-Silva, "Supporting tactical harvest planning decisions of major fruits through a multi-objective modeling approach by using exact methods," Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 251, p. 123929, 2024, doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123929.
S. Nahmias, Perishable Inventory Systems. Springer Science & Business Media, 2011, doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7999-5.
J. Beliën and H. Forcé, "Supply chain management of blood products: A literature review," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 217, pp. 1-16, 2012, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2011.05.026.
M. Yu and A. Nagurney, "Competitive food supply chain networks with application to fresh produce," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 224, pp. 273-282, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2012.07.033.
A. Rong, R. Akkerman, and M. Grunow, "An optimization approach for managing fresh food quality throughout the supply chain," International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 131, pp. 421-429, 2011, doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2009.11.026.
H. Flores and J. R. Villalobos, "A modeling framework for the strategic design of local fresh-food systems," Agricultural Systems, vol. 161, pp. 1-15, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2017.12.001.
B. Dan, T. Lei, X. Zhang, M. Liu, and S. Ma, "Modeling of the subsidy policy in fresh produce wholesale markets under yield uncertainty," Economic Modelling, vol. 126, p. 106413, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2023.106413.
Y. H. Chen, M. X. Chen, and A. K. Mishra, "Subsidies under uncertainty: Modeling of input-and output-oriented policies," Economic Modelling, vol. 85, pp. 39-56, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2019.05.005.
Khandelwal, C., & Barua, M. K., "Prioritizing circular supply chain management barriers using fuzzy AHP: case of the Indian plastic industry," Global Business Review, vol. 25, no. 1, pp. 232–251, 2024, doi: 10.1177/0972150920948818.
M. A. Hoque, M. N. Islam, and M. A. A. Khan, "A two-echelon inventory model for perishable products in a green supply chain with preservation technology," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 326, p. 129418, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129418.
G. Govindan, K. Rajendran, and A. K. P. Prakash, "Optimization of supply chain network for perishable food products considering shelf life and carbon footprint," Sustainable Production and Consumption, vol. 23, pp. 31-49, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2020.04.001.
R. Wang, C. Hu, and X. Liu, "Optimization of cold chain logistics network for fresh agricultural products," Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, vol. 143, p. 102086, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2020.102086.
S. Ali, M. Z. Khan, and A. Tiwari, "A hybrid approach for green vehicle routing problem with time windows considering sustainability aspects," Computers & Industrial Engineering, vol. 162, p. 107748, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107748.
C. H. Papadopoulos and N. P. Karakostas, "A green vehicle routing problem with environmental costs and multi-depot strategy," Sustainability, vol. 13, no. 10, p. 5589, 2021, doi: 10.3390/su13105589.
Sarrab, M., Pulparambil, S., and Awadalla, M., "Development of an IoT-based real-time traffic monitoring system for city governance," Global Transitions, vol. 2, pp. 230–245, 2020, doi: 10.1016/j.glt.2020.09.004.
A. K. Singh, A. Saxena, and R. K. Tiwari, "Green logistics and sustainable supply chain management: A literature review," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 283, p. 124660, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124660.
K. A. Bellman and R. M. Keller, "A survey of heuristic optimization strategies," IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics - Part A: Systems and Humans, vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 743-757, 2004, doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2004.829278.
R. Gera, P. Chadha, M. B. Nag, S. Sharma, H. Arora, A. Parvez, and L. Y. Sergeevna, "A systematic review of green supply chain management practices in firms," Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 69, pp. 535–542, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.08.366.
J. Zhang and B. Ding, "Multi-objective cold chain path optimization based on customer satisfaction," Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1806–1815, 2023, doi: 10.4236/jamp.2023.116116.
M. A. Nunes and P. R. V. Silva, "A robust approach for supply chain network design under uncertainty," Computers & Industrial Engineering, vol. 151, p. 106944, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106944.
B. Fahimnia, R. Z. Farahani, R. Marian, and L. Luong, "A review and critique on integrated production–distribution planning models and techniques," Journal of Manufacturing Systems, vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 1–19, 2013, doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2012.07.005.
A. G. Lagoudis, K. J. Angelides, and M. P. Karlaftis, "Multi-objective optimization for sustainable transportation and supply chain systems," *J. Transp. Geogr.*, vol. 34, pp. 96-107, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2013.12.005.
M. J. Fischer and A. D. Gehring, "Optimization in vehicle routing with time windows and sustainability constraints," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 256, no. 3, pp. 841-857, 2017, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2016.07.046.
N. Foroozesh, B. Karimi, and S. M. Mousavi, "Green-resilient supply chain network design for perishable products considering route risk and horizontal collaboration under robust interval-valued type-2 fuzzy uncertainty: A case study in food industry," Journal of Environmental Management, vol. 307, p. 114470, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114470.
F. M. Glover and K. Park, "Evolutionary algorithms for supply chain optimization," European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 238, no. 2, pp. 519-538, 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2014.03.023.
H. I. Turkay and D. L. Chao, "Carbon footprint reduction in perishable supply chains through intelligent routing," Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 340, p. 130776, 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.130776.
A. N. Rath, S. Mishra, and R. K. Jena, "A decision support system for supply chain risk management using fuzzy TOPSIS," Computers & Industrial Engineering, vol. 163, p. 107806, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107806.
W. Wang, Z. Sun, and X. Yang, "An adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for green vehicle routing problem with mixed fleet," Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, vol. 145, p. 102132, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2020.102132.
D. P. Bertsekas, Dynamic Programming and Optimal Control, 4th ed. Belmont, MA, USA: Athena Scientific, 2017.
A. P. Dantzig and R. H. Fulkerson, "Minimizing the number of tankers to meet a fixed schedule," Naval Research Logistics Quarterly, vol. 1, pp. 217-222, 1954, doi: 10.1002/nav.3800010209.
J. R. Birge and F. Louveaux, Introduction to Stochastic Programming, 2nd ed. New York, NY, USA: Springer, 2011, doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0237-4.
H. E. Garcia, K. J. Carlson, and J. M. O'Brien, "Optimization approaches for sustainable energy management," Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 139, p. 110689, 2021, doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2020.110689.
L. S. Lasdon, Optimization Theory for Large Systems. New York, NY, USA: Dover Publications, 2002.
S. J. Wright, Primal-Dual Interior-Point Methods. Philadelphia, PA, USA: SIAM, 1997, doi: 10.1137/1.9781611971453.
M. P. Johnson and H. S. Green, "Optimization techniques for green supply chain design," Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 8, p. 3254, 2020, doi: 10.3390/su12083254.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Teshome Bekele Dagne

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
In submitting the manuscript to the journal, the authors certify that:
- They are authorized by their co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- The work described has not been formally published before, except in the form of an abstract or as part of a published lecture, review, thesis, or overlay journal. Please also carefully read the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) Author Guidelines at http://journal2.uad.ac.id/index.php/ijio/about/submissions#onlineSubmissions
- That it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere,
- That its publication has been approved by all the author(s) and by the responsible authorities tacitly or explicitly of the institutes where the work has been carried out.
- They secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- They agree to the following license and copyright agreement.
Copyright
Authors who publish with the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

1.png)

