Multi-objective elitist spotted hyena resource optimized flexible job shop scheduling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/ijio.v5i1.8743Keywords:
Job shop scheduling, Multi-objective Elitist Spotted Hyena optimization, Rate-Monotonic preemptive Scheduling, Levenberg–Marquardt methodAbstract
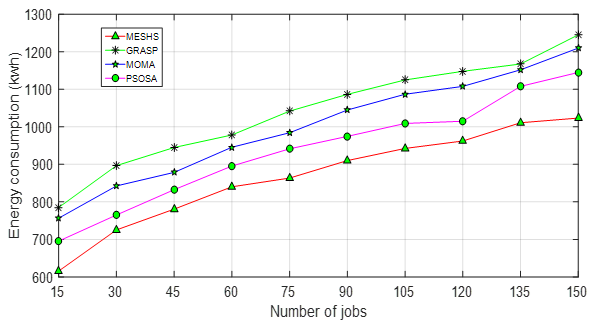
The job shop scheduling problem (JSSP) has drained a lot of consideration since it is one of the most important optimization problems in the manufacturing domain. The scheduling method is crucial for optimizing the objective of minimizing makespan among thousands of jobs, but evaluating machine capacity for achieving this goal remains challenging despite the development of various population-based optimization algorithms for job shop scheduling problems. To improve the efficiency of Job shop scheduling, a novel Multi-objective Elitist Spotted Hyena Monotonic Scheduling (MESHS) technique is introduced. The proposed MESHS technique includes two major processes: machine selection and operation sequences. The number of jobs is considered for solving the scheduling problem. First, the machine selection is performed by applying the Multi-objective Elitist Spotted Hyena optimization technique. The optimization technique selects the optimal machines parallelly based on multiple objective functions such as energy consumption, CPU utilization, and job completion time. The fitness of every machine is calculated based on these multiple objective functions using Levenberg–Marquardt method. Then the Elitist strategy is applied to select the optimal machine based on fitness. After the machine selection, the rate-monotonic preemptive scheduling is modeled to provide a robust operation sequence by assigning high-priority jobs to the optimal machines. As a result, efficient job scheduling is achieved with minimum time. Finally, the experimental valuation is carried out using a benchmark OR-Library dataset with different factors such as job shop scheduling efficiency, job scheduling time, makespan, and memory consumption concerning a number of jobs.
References
A. Baykasoglu and F. S. Madenoglu, "Greedy randomized adaptive search procedure for simultaneous scheduling of production and preventive maintenance activities in dynamic flexible job shops," Soft Computing, vol. 25, pp. 14893–14932, 2021, doi: 10.1007/s00500-021-06053-0
C. Lu, B. Zhang, L. Gao, J. Yi, and J. Mou, "A Knowledge-Based Multi-objective Memetic Algorithm for Green Job Shop Scheduling With Variable Machining Speeds," IEEE Systems Journal, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 844–855, 2022, doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3076481
D. B. M. M. Fontes, S. M. Homayouni, and J. F. Gonçalves, "A hybrid particle swarm optimization and simulated annealing algorithm for the job shop scheduling problem with transport resources," European Journal of Operational Research, pp. 1-18, 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2022.09.006
P. Schworm, X. Wu, M. Glatt, and J. C. Aurich, "Solving flexible job shop scheduling problems in manufacturing with Quantum Annealing," Production Engineering, pp. 1-11, 2022, doi: 10.1007/s11740-022-01145-8
E. Jiang, L. Wang, and J. Wang, "Decomposition-based multi-objective optimization for energy-aware distributed hybrid flow shop scheduling with multiprocessor tasks," Tsinghua Science and Technology, vol. 26, no. 5, pp. 646–663, 2021, doi: 10.26599/TST.2021.9010007
F. Zhang, Y. Mei, S. Nguyen, and M. Zhang, "Evolving Scheduling Heuristics via Genetic Programming With Feature Selection in Dynamic Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling," IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, vol. 51, no. 4, pp. 1797–1811, 2021, doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3024849
Y. Wang and Q. Zhu, "A Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem With Sequence-Dependent Setup Times and Job Lag Times," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 104864–104873, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3096007
S.-C. Horng and S.-S. Lin, "Apply Ordinal Optimization to Optimize the Job-Shop Scheduling Under Uncertain Processing Times," Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, vol. 47, 2022, pp. 9659-9671, doi: 10.1007/s13369-021-06317-9
W. Xiuli, P. Junjian, X. Zirun, Z. Ning, and W. Shaomin, "An improved multi-objective optimization algorithm for solving flexible job shop scheduling problem with variable batches," Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 272–285, 2021, doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000024
Z. C. Cao, C. Lin, and M. Zhou, "A Knowledge-Based Cuckoo Search Algorithm to Schedule a Flexible Job Shop With Sequencing Flexibility," IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 56–69, 2021, doi: 10.1109/TASE.2019.2945717
X. Liu, J. Chen, X. Huang, S. Guo, S. Zhang, and M. Chen, "A New Job Shop Scheduling Method for Remanufacturing Systems Using Extended Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 132429–132441, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3114712
F. Zhang, Y. Mei, S. Nguyen, and M. Zhang, "Correlation Coefficient-Based Recombinative Guidance for Genetic Programming Hyperheuristics in Dynamic Flexible Job Shop Scheduling," IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 552–566, 2021, doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2021.3056143
H. Wei, S. Li, H. Quan, D. Liu, S. Rao, C. Li, and J. Hu, "Unified Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm for Energy Efficient Job Shop Scheduling," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 54542–54557, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3070981
A. Vela, J. M. Cruz-Duarte, J. C. Ortiz-Bayliss, and I. Amaya, "Beyond Hyper-Heuristics: A Squared Hyper-Heuristic Model for Solving Job Shop Scheduling Problems," IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 43981–44007, 2022, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3169503
J. Fang, "An Effective Hybrid Multi-objective Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem Based on Improved Genetic Algorithm," Scientific Programming, vol. 2022, pp. 1-10, 2022, doi: 10.1155/2022/2120944
A. Ham, M.-J. Park, and K. M. Kim, "Energy-Aware Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Using Mixed Integer Programming and Constraint Programming," Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2021, pp. 1-12, 2021, doi: 10.1155/2021/8035806
P. Soofi, M. Yazdani, M. Amiri, and M. A. Adibi, "Robust Fuzzy-Stochastic Programming Model and Meta-Heuristic Algorithms for Dual-Resource Constrained Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem Under Machine Breakdown," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 155740–155762, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3126820
L. He, R. Chiong, W. Li, S. Dhakal, Y. Cao, and Y. Zhang, "Multi-objective Optimization of Energy-efficient Job-Shop Scheduling with Dynamic Reference Point-based Fuzzy Relative Entropy," IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 600–610, 2022, doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3056425
J. Liu, Z. Sui, X. Li, and J. Yang, "A Bayesian-Grouping Based Hybrid Distributed Cooperative Evolutionary Optimization for Large-Scale Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 69114–69126, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3076732
X. Liang, J. Chen, X. Gu, and M. Huang, "Improved Adaptive Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm With Elite Strategy for Solving Multi-Objective Flexible Job-Shop Scheduling Problem," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 106352–106362, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3098823
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 A. N. Senthilvel, T. Hemamalini , G. Geetha

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
In submitting the manuscript to the journal, the authors certify that:
- They are authorized by their co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- The work described has not been formally published before, except in the form of an abstract or as part of a published lecture, review, thesis, or overlay journal. Please also carefully read the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) Author Guidelines at http://journal2.uad.ac.id/index.php/ijio/about/submissions#onlineSubmissions
- That it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere,
- That its publication has been approved by all the author(s) and by the responsible authorities tacitly or explicitly of the institutes where the work has been carried out.
- They secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- They agree to the following license and copyright agreement.
Copyright
Authors who publish with the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

1.png)

