Minimizing production cost for kendang djembe production through goal programming model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/ijio.v3i2.6658Keywords:
Goal programming, Optimization, LingoAbstract
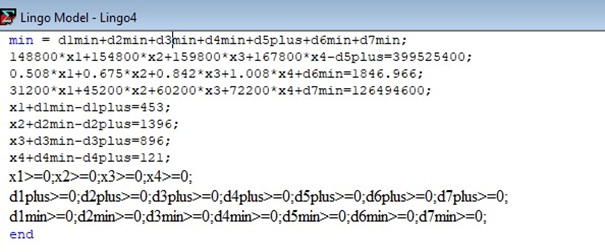
Kendang djembe is a percussion instrument played by striking with the fingers and palms. The body of the kendang djembe is generally made of wood and shaped like a cup or mug, carved either by machine or traditionally only by hand. This problem affects the production costs, the employee working house, and the profit of kendang djembe. Customer orders and requirements determine the production process for kendang djembe. It leads to fluctuations in market demand, affecting production costs and the working hours of kendang djembe employees. As a result, employees work overtime when orders rush in, resulting in poor product finishes such as crude engraving and painting. This research aims to minimize the production cost of kendang djembe, maximize the employee working hours, and maximize the profit by using the goal programming method. Goal programming is applied to decide the number of kendang djembe, the minimum production cost, and the time for each kendang djembe. The result of this research is that CV. Maharani Abadi has to make 237 units of kendang djembe paintings, 1266 kendang djembe carvings, 870 kendang djembe painting carvings, and 91 kendang djembe deep carvings. CV. Maharani spent a production cost of Rp 399,413,400, with the employee working 1846.36 hours, and obtained a maximum profit of Rp 126,526,600. This research helps the company to avoid unprofitable options in the production process of kendang djembe.
References
A. Eunike , N. W. Setyanto, R. Yuwinarti, I. Hamdala, R. Lukudono, and A. Fanani, Perencanaan Produksi dan Pengendalian Persediaan. Malang, Jawa Timur: UB Press, 2021. E. S. Buffa and R. K. Sarin, Modern Production Operations Management, New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1987.
E. S. Buffa and R. K. Sarin, Modern Production Operations Management, New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1987.
E. Suciyati. Analisis Perencanaan Kapasitas Produksi Dengan Metode Break Even Point Pada Ud Sinar Logam Jaya Kabupaten Tegal. Tegal, Indonesia: Universitas Pancasakti
A. Surachman, and Murti, Operations Research, Indonesia: Media Nusa Kreatif, 2015.
M. K. Zuhanda, S. Suwilo, O. S. Sitompul, and M. Mardingsih, “Goal programming method in optimizing course student admission, operational costs and profits,” Journal Of Informatics And Telecommunication Engineering, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 286–294, 2022.
F. Salas-Molina and J. A. Rodríguez-Aguilar, “Data-driven multiobjective decision-making in cash management,” EURO Journal on Decision Processes, vol. 6, no. 1-2, pp. 77–91, Jun. 2018.
Y. Yan, Y. Zhang, W. Hu, X.-jun Guo, C. Ma, Z.-ang Wang, and Q. Zhang, “A multiobjective evolutionary optimization method based critical rainfall thresholds for debris flows initiation,” Journal of Mountain Science, vol. 17, no. 8, pp. 1860–1873, 2020.
S. Biswas, S. G. Anavatti, and M. A. Garratt, “Multiobjective mission route planning problem: a neural network-based forecasting model for mission planning,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 430–442, Dec. 2021.
Y. Zhang, J. Wang, and H. Lu, “Research and application of a novel combined model based on multiobjective optimization for multistep-ahead electric load forecasting,” Energies, vol. 12, no. 10, p. 1931, 2019.
J. Wang, H. Li, Y. Wang, and H. Lu, “A hesitant fuzzy wind speed forecasting system with novel defuzzification method and multi-objective optimization algorithm,” Expert Systems with Applications, vol. 168, p. 114364, Apr. 2021. 0447
Y. Yang, “Clustering and prediction analysis of the coordinated development of China’s regional economy based on immune genetic algorithm,” Complexity, vol. 2021, pp. 1–12, Mar. 2021.
B. Luo, X. Liu, F. Zhang, and P. Guo, “Optimal management of cultivated land coupling remote sensing-based expected irrigation water forecasting,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 308, p. 127370, Jul. 2021.
Hamta, M. Ehsanifar, and J. Sarikhani, “Presenting a goal programming model in the timecost-quality trade-off,” International Journal of Construction Management, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–11, Feb. 2018.
S. Mulyono, Riset Operasi, Jakarta, Indonesia: UI Press, 2004.
M. K. Zuhanda, Muhathir, and D. M. Hutauruk, “Priority analysis of decision making in social entrepreneurship,” IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSRJEN), vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 14–26, Jan. 2020.
Siswanto, Operation Research Jilid 1, vol. 14, Indonesia: Erlangga, 2007, pp. 113-120.
S. Mardliyah, M. Y. Fajar, and F. H. Badruzzaman, “Penggunaan forecasting dan goal programming dalam optimasi perencanaan produksi beras,” Bandung Conference Series: Mathematics, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 83–93, Jan. 2022.
S. Gupta and S. Sinha, “Academic staff planning, allocation and optimization using genetic algorithm under the framework of fuzzy goal programming,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 172, pp. 900–905, 2020.
Y. A. Titilias, L. Linawati, and H. A. Parhusip, “optimasi perencanaan produksi kayu lapis pt. xxx menggunakan metode goal programming,” Indonesian Journal of Mathematics and Natural Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 13–19, Apr. 2018.
S. Gita, Optimasi perencanaan produksi kopi bubuk dengan metode goal programming berbasis qm for windows. Lampung, Indonesia: UIN Raden Intan Repository, 2018.
A.A. Marine., “optimasi perencanaan produksi dengan metode goal programming di ikm 3g bareng – jombang”, in Jurnal Valtech, 2018. [Online]. Available: https://ejournal.itn.ac.id/index.php/valtech/article/view/57.
F. Syahputra and W. Anggraeni, “Pemilihan supplier menggunakan metode relaxed-normalized goal programming untuk mengoptimalkan proses pengadaan produk (studi kasus: giant ekstra diponegoro surabaya)”, in Jurnal Teknik ITS, Vol 5 No. 1, 2016.
M. K. Zuhanda, S. Suwilo, O. S. Sitompul, and M. Mardingsih, “Goal programming method in optimizing course student admission, operational costs and profits,” Journal Of Informatics And Telecommunication Engineering, vol. 5, no. 2, pp. 286–294, 2022.
A. Wijaya, Pengantar Reset Operasi, Jakarta, Indonesia: Mitra Wacana Media, 2003.
A. Rangkuti, 7 Model Riset Operasi dan Aplikasinya, Surabaya, Indonesia: Brilian Internasional, 2013.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2022 Nabila Puspanola, Sumiati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
License and Copyright Agreement
In submitting the manuscript to the journal, the authors certify that:
- They are authorized by their co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- The work described has not been formally published before, except in the form of an abstract or as part of a published lecture, review, thesis, or overlay journal. Please also carefully read the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) Author Guidelines at http://journal2.uad.ac.id/index.php/ijio/about/submissions#onlineSubmissions
- That it is not under consideration for publication elsewhere,
- That its publication has been approved by all the author(s) and by the responsible authorities tacitly or explicitly of the institutes where the work has been carried out.
- They secure the right to reproduce any material that has already been published or copyrighted elsewhere.
- They agree to the following license and copyright agreement.
Copyright
Authors who publish with the International Journal of Industrial Optimization (IJIO) agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

1.png)

