Sentiment Analysis of the Increase in Fuel Prices Using Random Forest Classifier Method
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v5i1.7414Keywords:
BBM, Random Forest, Preprocessing, Streamlit, YouTubeAbstract
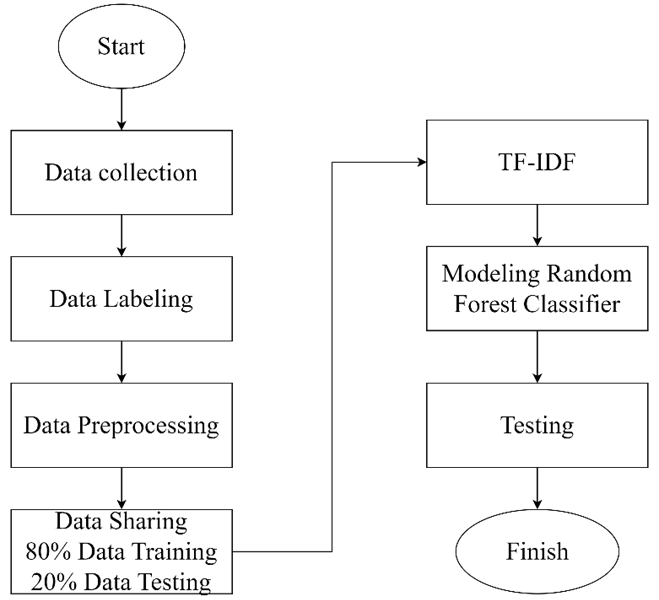
This research focuses on examining how the economy in Indonesia is affected by the increasing fuel prices, with a particular emphasis on the impact on the lower and middle-income populations. The announcement made by President Jokowi and his ministers about the fuel price hikes has spurred public reactions on social media platforms. The rise in fuel costs has a notable impact on people's livelihoods, especially concerning the surge in prices of essential goods. Sentiment analysis measures public opinion about the increase in fuel prices. The data taken from social media needs to be more balanced. The data is labeled with two identifications, “negative”, “positive” and “neutral”. The method used in sentiment analysis is the random forest method. This research contributes to determining the number of trees used in the model formation with public opinion data. The F1-score measurement result on the model is achieved at a value of 60%.
References
N. T. S. Saptadi, A. Suyuti, A. A. Ilham and I. Nurtanio, “Energy Potential Estimation System Model To Produce Alternative Energy Briquettes,” 2022 International Conference on Informatics Electrical and Electronics (ICIEE), pp. 1-7, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIEE55596.2022.10009988.
M. Herlina, “Panel Cointegration Analysis in Determining Relationship of Agricultural Commodity and Oil Fuel Price in Indonesia,” Indonesian Journal of Statistics and Its Applications, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 341–358, 2020, https://doi.org/10.29244/ijsa.v4i2.662.
S. Sultan, J. J. Sarungu, A. M. Soesilo and S. A. T. Rahayu, “Oil price and Indonesian economic growth,” Problems and Perspectives in Management, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 152-162, 2019, https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.17(1).2019.14.
P. A. Rakhmanto, “Simulation of the Impacts of Fuel Pricing Policies towards Inflation in Indonesia,” International Journal of Multidisciplinary and Current Educational Research (IJMCER), vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 24–31, 2022, https://www.ijmcer.com/volume-4-issue-4/.
E. Prabowo, H. Harianto, B. Juanda and D. Indrawan, “The Economic Price of Liquid Petroleum Gas, Poverty and Subsidy Removal Compensation Scenario in Indonesia,” International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, vol. 12, no. 5, pp. 169–177, 2022, https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.13356.
T. Wang and B. Lin, “Fuel consumption in road transport: A comparative study of China and OECD countries,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 206, pp. 156-170, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.092.
A. Akhmad and A. Amir, “Research of fuel oil supply and consumption in indonesia,” International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 13–20, 2018, https://econjournals.com/index.php/ijeep/article/view/6448.
B. Kharisma, “Can A School Operational Assistance Fund Program ( BOS ) Reduce School Drop-Outs During The Post-Rising Fuel Prices In Indonesia ? Evidence From Indonesia,” Munich Personal RePEc Archive, no. 70041, pp. 1–14, 2016, https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/70041/.
A. N. Kurniawan, A. I. Rifai and M. Rizal. S, “Phenomena of Transportation to Work Mode Choice , Due to The Increase of Oil Prices in Indonesia : A Case Light Rail Transit Depot Project Office-Jakarta,” CITIZEN:JurnalIlmiahMultidisiplinIndonesia, vol. 2, no. 5, pp. 785–793, 2022, https://journal.das-institute.com/index.php/citizen-journal/article/view/193.
A. Akhmad, B. Romadhoni, K. Karim, M. J. Tajibu and M. Syukur, “The Impact of Fuel Oil Price Fluctuations on Indonesia’s Macro Economic Condition,” International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 277–282, 2019, https://doi.org/10.32479/ijeep.7470.
R. A. Maisal, A. N. Hidayanto, N. F. Ayuning Budi, Z. Abidin and A. Purbasari, “Analysis of Sentiments on Indonesian YouTube Video Comments: Case Study of The Indonesian Government's Plan to Move the Capital City,” 2019 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS), pp. 121-124, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIMCIS48181.2019.8985228.
Y. Pratama, A. R. Tampubolon, L. D. Sianturi, R. D. Manalu and D. F. Pangaribuan, “Implementation of sentiment analysis on Twitter using Naïve Bayes algorithm to know the people responses to debate of DKI Jakarta governor election,” In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, vol. 1175, no. 1, p. 012102, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1175/1/012102.
J. Asian, M. Dholah Rosita and T. Mantoro, “Sentiment Analysis for the Brazilian Anesthesiologist Using Multi-Layer Perceptron Classifier and Random Forest Methods,” JOIN (Jurnal Online Informatika), vol. 7, no. 1, p. 132, 2022, https://doi.org/10.15575/join.v7i1.900.
Y. Al Amrani, M. Lazaar and K. E. El Kadirp, “Random forest and support vector machine based hybrid approach to sentiment analysis,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 127, pp. 511–520, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.01.150.
X. Shu and Y. Ye, “Knowledge Discovery: Methods from data mining and machine learning,” Social Science Research, vol. 110, p. 102817, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssresearch.2022.102817.
P. Kaur, “Sentiment analysis using web scraping for live news data with machine learning algorithms,” Materials Today: Proceedings, vol. 65, pp. 3333-3341, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.05.409.
A. P. Widyassari, E. Noersasongko, A. Syukur and Affandy, “The 7-Phases Preprocessing Based On Extractive Text Summarization,” 2022 Seventh International Conference on Informatics and Computing (ICIC), pp. 1-8, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIC56845.2022.10006998.
N. O. F. Daeli and A. Adiwijaya, “Sentiment Analysis on Movie Reviews Using Information Gain and K-Nearest Neighbor,” Journal of Data Science and Its Applications, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 1–7, 2020, https://doi.org/10.34818/jdsa.2020.3.22.
S. Khomsah, R. D. Ramadhani and S. Wijaya, “The Accuracy Comparison Between Word2Vec and FastText On Sentiment Analysis of Hotel Reviews,” Jurnal RESTI (Rekayasa Sistem Dan Teknologi Informasi), vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 352–358, 2022, https://doi.org/10.29207/resti.v6i3.3711.
N. Saputra, K. Nurbagja and T. Turiyan, “Sentiment Analysis of Presidential Candidates Anies Baswedan and Ganjar Pranowo Using Naïve Bayes Method,” Jurnal Sisfotek Global, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 114-119, 2022, http://dx.doi.org/10.38101/sisfotek.v12i2.552.
F. Y. A'la, “Indonesian Sentiment Analysis towards MyPertamina Application Reviews by Utilizing Machine Learning Algorithms,” Journal of Informatics Information System Software Engineering and Applications (INISTA) vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 80–91, 2022, https://journal.ittelkom-pwt.ac.id/index.php/inista/article/view/838.
C. Ding et al., “Towards Burmese (Myanmar) morphological analysis: Syllable-based tokenization and part-of-speech tagging,” ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP), vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 1-34, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1145/3325885.
M. A. Fauzi, “Random forest approach fo sentiment analysis in Indonesian language,” Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 46–50, 2018, http://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v12.i1.pp46-50.
A. Ridwan, H. H. Nuha and R. Dharayani, “Sentiment Analysis of Floods on Twitter Social Media Using the Naive Bayes Classifier Method with the N-Gram Feature,” 2022 International Conference on Data Science and Its Applications (ICoDSA), pp. 114-118, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICoDSA55874.2022.9862827.
S. Taj, B. B. Shaikh and A. Fatemah Meghji, “Sentiment Analysis of News Articles: A Lexicon based Approach,” 2019 2nd International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET), pp. 1-5, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICOMET.2019.8673428.
S. Pebiana et al., “Experimentation Of Various Preprocessing Pipelines For Sentiment Analysis On Twitter Data About New Indonesia’s Capital City Using SVM And CNN,” 2022 25th Conference of the Oriental COCOSDA International Committee for the Co-ordination and Standardisation of Speech Databases and Assessment Techniques (O-COCOSDA), pp. 1-6, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/O-COCOSDA202257103.2022.9997982.
J. Singh and V. Gupta, “A novel unsupervised corpus-based stemming technique using lexicon and corpus statistics,” Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 180, pp. 147-162, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.05.025.
M. Guia, R. R. Silva and J. Bernardino, “Comparison of Naive Bayes, support vector machine, decision trees and random forest on sentiment analysis,” In Proceedings of the 11th International Joint Conference on Knowledge Discovery, Knowledge Engineering and Knowledge Management - KDIR, pp. 525–531, 2019, https://doi.org/10.5220/0008364105250531.
A. Y. Clara, A. Adiwijaya and M. D. Purbolaksono, “Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis on Beauty Product Review Using Random Forest,” Journal of Data Science and Its Applications, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 67–77, 2020, https://doi.org/10.34818/jdsa.2020.3.58.
M. M. Chen and M. C. Chen, “Modeling road accident severity with comparisons of logistic regression, decision tree and random forest,” Information, vol. 11, no. 5, p. 270, 2020, https://doi.org/10.3390/info11050270.
A. Nayak and S. Natarajan, “Comparative research of Naïve Bayes, Support Vector Machine and Random Forest Classifiers in Sentiment Analysis of Twitter Feeds,” International Journal of Advanced Studies in Computer Science and Engineering, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 14–17, 2016, http://www.ijascse.org/volume-5-theme-based-issue-1/Support_vector_machine.pdf.
V. Jain and A. Phophalia, “M-ary Random Forest-A new multidimensional partitioning approach to Random Forest,” Multimedia Tools and Applications, vol. 80, pp. 35217-35238, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-10047-9.
M. M. Kholil, F. Alzami and M. A. Soeleman, “AdaBoost Based C4.5 Accuracy Improvement on Credit Customer Classification,” 2022 International Seminar on Application for Technology of Information and Communication (iSemantic), pp. 351-356, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1109/iSemantic55962.2022.9920463.
M. N. Tentua and A. Sihabuddin, “Improved C4. 5 Algorithm Using the L’Hospital Rule and Prunning on the Recommendation System,” vol. 8, no. 11, 2019, http://www.ijstr.org/final-print/nov2019/Improved-C45-Algorithm-Using-The-Lhospital-Rule-And-Prunning-On-The-Recommendation-System.pdf.
N. Bahrawi, “Sentiment Analysis Using Random Forest Algorithm-Online Social Media Based,” Journal of Information Technology and Its Utilization, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 29-33, 2019, https://doi.org/10.30818/jitu.2.2.2695.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Karandi Nurbagja, Nurirwan Saputra, Ahmad Riyadi, Meilany Nonsi Tentua

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


