Mitigating Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) Attacks in Cloud Computing Using an AI-Driven Cost-Aware Defense System
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v8i1.15187Keywords:
Economic Denial of Sustainability, Cloud Security, Cost-Aware Defense, Deep Learning, Trust-Based Access Control, SDNAbstract
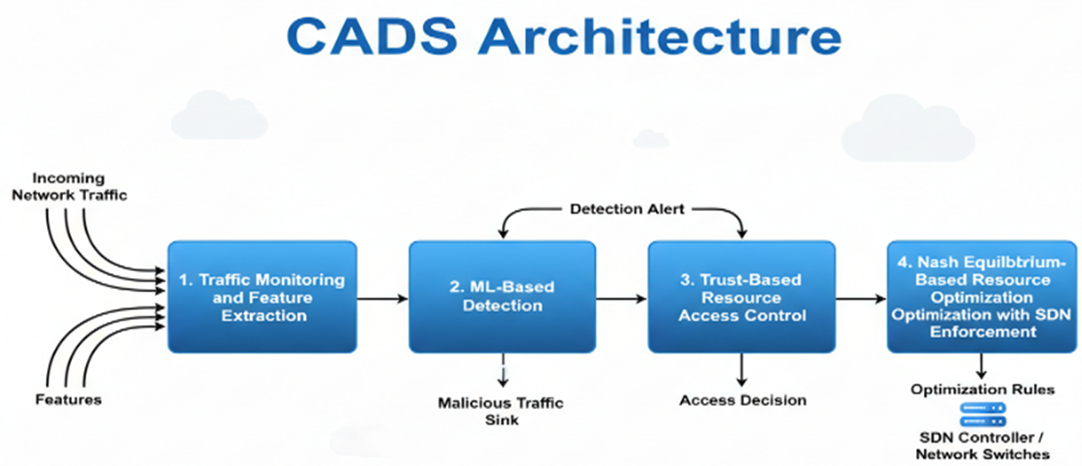
The pay-per-use billing model of cloud computing makes cloud infrastructures highly vulnerable to Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) attacks, where adversaries exploit auto-scaling mechanisms to trigger excessive resource consumption and inflated operational costs. Existing mitigation approaches, such as rate limiting and conventional anomaly detection, struggle to accurately distinguish legitimate traffic from attack-traffic requests, often leading to false negative alarm and unnecessary financial overhead. This paper proposes a Cost-Aware Adaptive Defense System (CADS), a novel artificial intelligence-driven (AI-driven) defense system that integrates deep learning-based (DL-based) traffic classification, Trust-based resource access control, and Software-Defined Networking-based (SDN-based) traffic filtering to mitigate EDoS attacks while preserving economic sustainability. The Trust-based access control mechanism dynamically assigns trust scores to incoming requests and restricts suspicious entities from triggering auto-scaling, thereby preventing fraudulent resource allocation. The proposed defense system introduces a lightweight computational overhead of approximately 85 ms for detection and 210 ms for mitigation response, ensuring real-time protection with minimal performance impact. Experimental evaluation was conducted in an OpenStack-based simulated cloud environment, modeling multiple EDoS attack strategies, including HTTP flood, ICMP-based, and workload-based attacks. Results demonstrate that CADS achieves a detection performance such as 97.1% for (F1-score), 97.5% for Recall and 96.8 for Precision, indicates significantly reducing missed attacks and false alarm. More importantly, CADS reduces overall cloud billing costs by approximately 25% compared to state-of-the-art EDoS mitigation mechanisms, such as Advanced EDoS Attack Defense Shell (EDoS-ADS) and Multi-head Attention Network (MAN-EDoS). The results highlight the practical effectiveness of CADS in enhancing cloud security resilience while substantially lowering operational expenses for cloud service providers. Although CADS has not been tested in real-world environments, it demonstrates strong performance under simulated conditions. Future work will focus on large-scale real-world deployments and the integration of reinforcement learning techniques to adapt to evolving attack patterns.
References
T. H. Aldhyani and H. Alkahtani, "Artificial intelligence algorithm-based economic denial of sustainability attack detection systems: Cloud computing environments," Sensors, vol. 22, no. 13, p. 4685, 2022, https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134685.
F. Briatore and M. Braggio, "Edge, Fog and Cloud Computing framework for flexible production," Procedia Computer Science, vol. 253, pp. 2206-2218, 2025, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2025.01.281.
P. T. Dinh and M. Park, "R-EDoS: Robust Economic Denial of Sustainability Detection in an SDN-Based Cloud Through Stochastic Recurrent Neural Network," IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 35057-35074, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3061601.
Z. A. Baig, S. M. Sait, and F. Binbeshr, "Controlled access to cloud resources for mitigating Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) attacks," Computer Networks, vol. 97, pp. 31-47, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2016.01.002.
H. Abbasi, N. Ezzati-Jivan, M. Bellaiche, C. Talhi, and M. R. Dagenais, "Machine learning-based EDoS attack detection technique using execution trace analysis," Journal of Hardware and Systems Security, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 164-176, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41635-018-0061-2.
P. T. Dinh and M. Park, "Dynamic Economic-Denial-of-Sustainability (EDoS) Detection in SDN-based Cloud," in 2020 Fifth International Conference on Fog and Mobile Edge Computing (FMEC), pp. 62-69, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/FMEC49853.2020.9144972.
A. Agarwal, A. Prasad, R. Rustogi, and S. Mishra, "Detection and mitigation of fraudulent resource consumption attacks in cloud using deep learning approach," Journal of Information Security and Applications, vol. 56, p. 102672, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2020.102672.
C.-N. Nhu and M. Park, "Two-Phase Deep Learning-Based EDoS Detection System," Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 21, p. 10249, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/app112110249.
S. Ribin Jones and N. Kumar, "EDoS-BARRICADE: A Cloud-Centric Approach to Detect, Segregate and Mitigate EDoS Attacks," in International Conference on Communication, Computing and Electronics Systems, pp. 579-592, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-33-4909-4_44.
K. Lalropuia, "Availability and reliability analysis of cloud computing under economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attack: a semi-Markov approach," Cluster Computing, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 2177-2191, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03257-9.
X. Xu, J. Li, H. Yu, L. Luo, X. Wei, and G. Sun, "Towards Yo-Yo attack mitigation in cloud auto-scaling mechanism," Digital communications and networks, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 369-376, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcan.2019.07.002.
H. I. H. Alsaadi, M. K. Al-Anni, and F. E. K. Al-Khuzaie, "Deep learning to mitigate economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attacks: cloud computing," in 2023 3rd International Conference on Emerging Smart Technologies and Applications (eSmarTA), pp. 1-7, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/eSmarTA59349.2023.10293405.
J. Idziorek, M. Tannian, and D. Jacobson, "Attribution of fraudulent resource consumption in the cloud," in 2012 IEEE fifth international conference on cloud computing, pp. 99-106, 2012, https://doi.org/10.1109/CLOUD.2012.23.
H. Wang, Z. Xi, F. Li, and S. Chen, "WebTrap: A dynamic defense scheme against economic denial of sustainability attacks," in 2017 IEEE Conference on Communications and Network Security (CNS), pp. 1-9, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/CNS.2017.8228640.
A. Koduru, T. Neelakantam, and S. M. S. B, "Detection of Economic Denial of Sustainability Using Time Spent on a Web Page in Cloud," in 2013 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing in Emerging Markets (CCEM), pp. 1-4, 2013, https://doi.org/10.1109/CCEM.2013.6684433.
G. Capasso and A. Esposito, "Detection of DoS Attacks in Cloud Computing: A Machine Learning Approach," in International Conference on Broadband and Wireless Computing, Communication and Applications, pp. 275-284, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-76452-3_26.
J. Britto Dennis and M. Shanmuga Priya, "Deep belief network and support vector machine fusion for distributed denial of service and economical denial of service attack detection in cloud," Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, vol. 34, no. 1, p. e6543, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1002/cpe.6543.
V. Ta and M. Park, "MAN-EDoS: A Multihead Attention Network for the Detection of Economic Denial of Sustainability Attacks," Electronics, vol. 10, no. 20, p. 2500, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10202500.
F. Z. Chowdhury, L. B. M. Kiah, M. A. M. Ahsan, and M. Y. I. B. Idris, "Economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) mitigation approaches in cloud: Analysis and open challenges," in 2017 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (ICECOS), pp. 206-211, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICECOS.2017.8167135.
K. Lalropuia and V. Khaitan, "Availability and reliability analysis of cloud computing under economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attack: a semi-Markov approach," Cluster Computing, vol. 24, pp. 2177-2191, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10586-021-03257-9.
F. Z. Chowdhury, M. Y. I. Idris, L. M. Kiah, and M. A. M. Ahsan, "EDoS eye: A game theoretic approach to mitigate economic denial of sustainability attack in cloud computing," in 2017 IEEE 8th Control and System Graduate Research Colloquium (ICSGRC), pp. 164-169, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSGRC.2017.8070588.
A. Karthika and N. Muthukumaran, "An ADS-PAYG approach using trust factor Against economic denial of sustainability attacks in cloud storage," Wireless Personal Communications, vol. 122, no. 1, pp. 69-85, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-021-08889-z.
P. T. Dinh and M. Park, "Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) Detection using GANs in SDN-based Cloud," in 2020 IEEE Eighth International Conference on Communications and Electronics (ICCE), pp. 135-140, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCE48956.2021.9352082.
P. Singh, S. Manickam and S. U. Rehman, "A survey of mitigation techniques against Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) attack on cloud computing architecture," Proceedings of 3rd International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization, pp. 1-4, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRITO.2014.7014767.
Y. Alghofaili, A. Albattah, N. Alrajeh, M. A. Rassam, and B. A. S. Al-Rimy, "Secure cloud infrastructure: A survey on issues, current solutions, and open challenges," Applied Sciences, vol. 11, no. 19, p. 9005, 2021, https://doi.org/10.3390/app11199005.
M. A. Sotelo Monge, J. Maestre Vidal, and L. J. García Villalba, "Entropy-based economic denial of sustainability detection," Entropy, vol. 19, no. 12, p. 649, 2017, https://doi.org/10.3390/e19120649.
P. Singh, S. U. Rehman, and S. Manickam, "Comparative analysis of state-of-the-art EDoS mitigation techniques in cloud computing environment," arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.13447, 2019, https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.13447.
B. B. Rao, S. Bulla, K. G. Rao, and K. Chandan, "HRF (HTTP request filtering): a new detection mechanism of EDOS attack on cloud," in 2019 International Carnahan Conference on Security Technology (ICCST), pp. 1-7, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/CCST.2019.8888431.
S. Q. A. Shah, F. Z. Khan, and M. Ahmad, "The impact and mitigation of ICMP based economic denial of sustainability attack in cloud computing environment using software defined network," Computer Networks, vol. 187, p. 107825, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2021.107825.
M. S. Hossain and M. S. Islam, "Economic Denial of Sustainability Attack Detection Using Machine Learning," in 2023 26th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT), pp. 1-6, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCIT60459.2023.10441045.
K. Lalropuia and V. Khaitan, "Game theoretic modeling of economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attack in cloud computing," Probability in the Engineering and Informational Sciences, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 1241-1265, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1017/S0269964821000334.
P. S. Bawa, S. U. Rehman, and S. Manickam, "Enhanced mechanism to detect and mitigate economic denial of sustainability (EDoS) attack in cloud computing environments," Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 51-58, 2017, https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2017.080907.
A. Shawahna, M. Abu-Amara, A. S. H. Mahmoud, and Y. Osais, "EDoS-ADS: An Enhanced Mitigation Technique Against Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) Attacks," IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 790-804, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/TCC.2018.2805907.
M. H. Khalil, M. Azab, A. Elsayed, W. Sheta, M. Gabr, and A. S. Elmaghraby, "Maintaining cloud performance under DDOS attacks," IJCNC, vol. 11, no. 6, pp. 1-22, 2019, https://doi.org/10.5121/ijcnc.2019.11601.
R. K. Deka, D. K. Bhattacharyya, and J. K. Kalita, "Ddos attacks: Tools, mitigation approaches, and probable impact on private cloud environment," Big Data Analytics for Internet of Things, pp. 285-319, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119740780.ch13.
R. Priyadarshini and R. K. Barik, “A deep learning based intelligent framework to mitigate DDoS attack in fog environment,” Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 825-831, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2019.04.010.
J. M. Vidal, M. A. S. Monge, and L. J. G. Villalba, "Detecting Workload-based and Instantiation-based Economic Denial of Sustainability on 5G environments," in Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Availability, Reliability and Security, pp. 1-8, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1145/3230833.3233247.
S. Nautiyal and S. Wadhwa, "A Comparative Approach to Mitigate Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) in a Cloud Environment," in 2019 4th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON), pp. 615-619, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1109/ISCON47742.2019.9036257.
S. Nautiyal, C. R. Krishna, and S. Wadhwa, "Mitigating Economic Denial of Sustainability (EDoS) in Cloud Environment using Genetic Algorithm and Artificial Neural Network," International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE), vol. 8, no. 10, pp. 3415-3421, 2019, https://doi.org/10.35940/ijitee.J9680.0881019.
N. Beigi-Mohammadi, M. Shtern and M. Litoiu, "Adaptive Load Management of Web Applications on Software Defined Infrastructure," in IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 488-502, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSM.2019.2948969.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Zubaidi Maytham Sahar Saeed, Anazida Binti Zainal, Fuad A. Ghaleb

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


