Multiagent based Power Management for Grid-connected Photovoltaic Source Using the Optimized Network Parameters From Butterworth Inertia Weight Particle Swarm Optimization
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/biste.v6i4.11391Keywords:
Multiagent, Energy Storage System, Photovoltaic, Butterworth, OptimizationAbstract
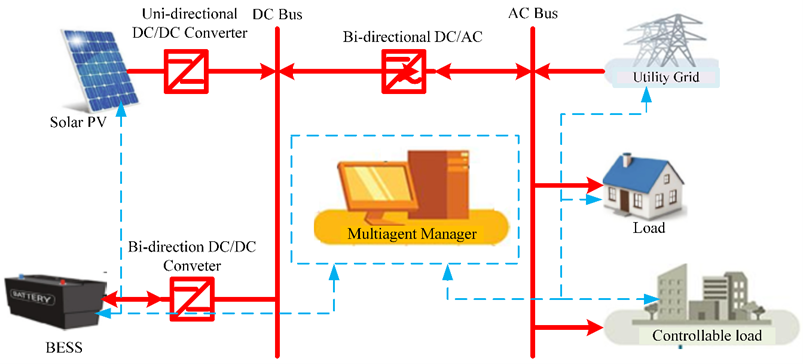
An efficient power management technique of a grid-connected renewable source proficiently coordinates the various controllable units necessary in the power system operation. It is achieved by responding to the dynamic load demand through efficient communication and advanced control structures. This paper presents a decentralized multiagent power management technique for a grid-connected photovoltaic/energy storage system using the optimized network parameters from the Butterworth inertial weight particle swarm optimization method. The power network is coordinated by intelligent agents and structured into a zonal generation and load multiagent system to update the load and power injected at different network buses. However, Butterworth inertial weighting function particle swarm optimization determines the optimized network parameters and the capacity of the connected energy sources fed into the multiagent system. The inertial weight of the optimization technique is patterned along the Butterworth filtering curve for holistic space search and improved convergence. Hence, the proposed technique solves the problem of inefficient optimization methods and provides a robust control and management system with agents capable of reorganizing and coping with the system's dynamic changes. The performance analysis of the IEEE 33-Bus distribution system shows an improved network coordinating method. The power loss reduction appreciated significantly from 65.42% to 68.58%, while the voltage deviation improved from 88.19% to 89.95% by integrating a renewable battery system. The voltage is maintained within the operational constraints of daily simulations. The method is targeted at efficient operation of distribution networks.
References
A. U. Adoghe, T. M. Adeyemi-Kayode, V. Oguntosin, and I. I. Amahia, “Performance evaluation of the prospects and challenges of effective power generation and distribution in Nigeria,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 3, p. 441, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14416.
N. Kanagaraj, M. Vijayakumar, M. Ramasamy, and O. Aldosari, “Energy Management and Power Quality Improvement of Hybrid Renewable Energy Generation System Using Coordinated Control Scheme,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, no. June, pp. 93254–93267, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3299035.
R. Debnath, V. Mittal, and A. Jindal, “A review of challenges from increasing renewable generation in the Indian Power Sector: Way forward for Electricity (Amendment) Bill 2020,” Energy Environ., vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 3–40, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X20986246.
S. Kawambwa and D. Mnyanghwalo, “A multi-agent-based symbiotic organism search algorithm for DG coordination in electrical distribution networks,” J. Electr. Syst. Inf. Technol., vol. 10, no. 1, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1186/s43067-023-00072-7.
W. Shi, D. Zhang, X. Han, X. Wang, T. Pu and W. Chen, "Coordinated operation of active distribution network, networked microgrids, and electric vehicle: A multi-agent PPO optimization method," in CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2023, https://doi.org/10.17775/CSEEJPES.2022.05640.
S. S. Ghazimirsaeid, M. S. Jonban, M. W. Mudiyanselage, M. Marzband, J. L. R. Martinez, and A. Abusorrah, “Multi-agent-based energy management of multiple grid-connected green buildings,” J. Build. Eng., vol. 74, no. May, p. 106866, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106866.
A. Al-Hinai and H. Haes Alhelou, “A multi-agent system for distribution network restoration in future smart grids,” Energy Reports, vol. 7, pp. 8083–8090, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2021.08.186.
T. Senjyu, Y. Miyazato, A. Yona, N. Urasaki, and T. Funabashi, “Optimal distribution voltage control and coordination with distributed generation,” IEEE Trans. Power Deliv., vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 1236–1242, 2008, https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2007.908816.
P. N. Vovos, A. E. Kiprakis, A. R. Wallace, and G. P. Harrison, “Centralized and distributed voltage control: Impact on distributed generation penetration,” IEEE Trans. Power Syst., vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 476–483, 2007, https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRS.2006.888982.
B. Zhang, D. Cao, W. Hu, A. M. Y. M. Ghias, and Z. Chen, “Physics-Informed Multi-Agent deep reinforcement learning enabled distributed voltage control for active distribution network using PV inverters,” Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 155, no. PB, p. 109641, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2023.109641.
A. Y. Hatata, E. O. Hasan, M. A. Alghassab, and B. E. Sedhom, “Centralized Control Method for Voltage Coordination Challenges With OLTC and D-STATCOM in Smart Distribution Networks Based IoT Communication Protocol,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, no. February, pp. 11903–11922, 2023, https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3242236.
M. Pérez Hernández, A. Puchkova, and A. K. Parlikad, “Multi-Agent Learning of Asset Maintenance Plans through Localised Subnetworks,” Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 127, no. PB, p. 107362, 2024, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107362.
H. Lan, S. Wen, Q. Fu, D. C. Yu, and L. Zhang, “Modeling analysis and improvement of power loss in microgrid,” Math. Probl. Eng., vol. 2015, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/493560.
E. Unamuno and J. A. Barrena, “Hybrid ac/dc microgrids - Part I: Review and classification of topologies,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 52, pp. 1251–1259, 2015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.194.
Y. Yoldaş, A. Önen, S. M. Muyeen, A. V. Vasilakos, and İ. Alan, “Enhancing smart grid with microgrids: Challenges and opportunities,” Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev., vol. 72, no. January, pp. 205–214, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.064.
M. S. Rahman, M. A. Mahmud, H. R. Pota, and M. J. Hossain, “Distributed multi-agent scheme for reactive power management with renewable energy,” Energy Convers. Manag., vol. 88, pp. 573–581, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.09.002.
H. K. Kang, I. Y. Chung, and S. Il Moon, “Voltage control method using distributed generators based on a multi-agent system,” Energies, vol. 8, no. 12, pp. 14009–14025, 2015, https://doi.org/10.3390/en81212411.
E. Shirazi and S. Jadid, “A multiagent design for self-healing in electric power distribution systems,” Electr. Power Syst. Res., vol. 171, no. February, pp. 230–239, 2019, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsr.2019.02.025.
E. Abbaspour, B. Fani, E. Heydarian-Forushani, and A. Al-Sumaiti, “A multi-agent based protection in distribution networks including distributed generations,” Energy Reports, vol. 8, pp. 163–174, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2022.10.394.
E. Xydas, C. Marmaras, and L. M. Cipcigan, “A multi-agent based scheduling algorithm for adaptive electric vehicles charging,” Appl. Energy, vol. 177, pp. 354–365, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.05.034.
Z. Liu, C. Su, H. K. Hoidalen, and Z. Chen, “A multiagent system-based protection and control scheme for distribution system with distributed-generation integration,” IEEE Trans. Power Deliv., vol. 32, no. 1, pp. 536–545, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/TPWRD.2016.2585579.
K. Mistry, “MSFL based determination of optimal size and location of distributed generation in radial distribution system,” Int. Conf. Electr. Electron. Optim. Tech. ICEEOT 2016, pp. 530–535, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/ICEEOT.2016.7755670.
M. A. Tolba, V. N. Tulsky, and A. A. Z. Diab, “Optimal sitting and sizing of renewable distributed generations in distribution networks using a hybrid PSOGSA optimization algorithm,” Conf. Proc. - 2017 17th IEEE Int. Conf. Environ. Electr. Eng. 2017 1st IEEE Ind. Commer. Power Syst. Eur. EEEIC / I CPS Eur. 2017, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1109/EEEIC.2017.7977441.
V. N. TUL’SKY, M. A. TOLBA, and A. S. VANIN, “Optimal Capacitor Allocations and Sizing in Radial Distribution Networks Using a Novel Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm,” Elektrichestvo, no. 6, pp. 16–23, 2017, https://doi.org/10.24160/0013-5380-2017-6-16-23.
P. A. Gkaidatzis, A. S. Bouhouras, D. I. Doukas, K. I. Sgouras, and D. P. Labridis, “Application and evaluation of UPSO to ODGP in radial Distribution Networks,” Int. Conf. Eur. Energy Mark. EEM, vol. 2016-July, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1109/EEM.2016.7521223.
M. Bechouat, M. Sedraoui, Y. Soufi, L. Yousfi, A. Borni, and S. Kahla, “Particle swarm optimization backstepping controller for a grid-connected PV/Wind Hybrid system,” J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev., vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 91–99, 2017, https://doi.org/10.25103/jestr.101.13.
M. Marzband, M. Ghadimi, A. Sumper, and J. L. Domínguez-García, “Experimental validation of a real-time energy management system using multi-period gravitational search algorithm for microgrids in islanded mode,” Appl. Energy, vol. 128, pp. 164–174, 2014, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.04.056.
M. H. Moradi and M. Abedini, “A combination of genetic algorithm and particle swarm optimization for optimal DG location and sizing in distribution systems,” Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 34, no. 1, pp. 66–74, 2012, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2011.08.023.
T. S. Tawfeek, A. H. Ahmed, and S. Hasan, “Analytical and particle swarm optimization algorithms for optimal allocation of four different distributed generation types in radial distribution networks,” Energy Procedia, vol. 153, pp. 86–94, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.10.030.
X. Zhu and H. Wang, “A new inertia weight control strategy for particle swarm optimization,” AIP Conf. Proc., vol. 1955, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5033759.
O. Olatunde, M. Y. Hassan, M. P. Abdullah, and H. A. Rahman, “Real-time multiperiod voltage control algorithm with OLTC and switched capacitors for smart distribution networks in the presence of energy storage system,” Int. Trans. Electr. Energy Syst., no. March, pp. 1–21, 2020, https://doi.org/10.1002/2050-7038.12475.
A. Hussain, S. M. Arif, M. Aslam, and S. D. A. Shah, “Optimal siting and sizing of tri-generation equipment for developing an autonomous community microgrid considering uncertainties,” Sustain. Cities Soc., vol. 32, no. September 2016, pp. 318–330, 2017, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scs.2017.04.004.
T. Kerdphol, K. Fuji, Y. Mitani, M. Watanabe, and Y. Qudaih, “Optimization of a battery energy storage system using particle swarm optimization for stand-alone microgrids,” Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst., vol. 81, pp. 32–39, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijepes.2016.02.006.
A. Chamba, C. Barrera-Singaña, and H. Arcos, “Optimal Reactive Power Dispatch in Electric Transmission Systems Using the Multi-Agent Model with Volt-VAR Control,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 13, pp. 1–25, 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/en16135004.
M. javad Aliabadi and M. Radmehr, “Optimization of hybrid renewable energy system in radial distribution networks considering uncertainty using meta-heuristic crow search algorithm,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 107, p. 107384, 2021, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2021.107384.
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Oladepo Olatunde, Ugwute Francis Okoro, Awofolaju Tolulope Tola

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).
This journal is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


