Analysis of House Price Determination in 13 G20 Countries: Random Effect Model
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/jampe.v2i2.7983Keywords:
House, Price, Macroeconomics , Random Effect ModelAbstract
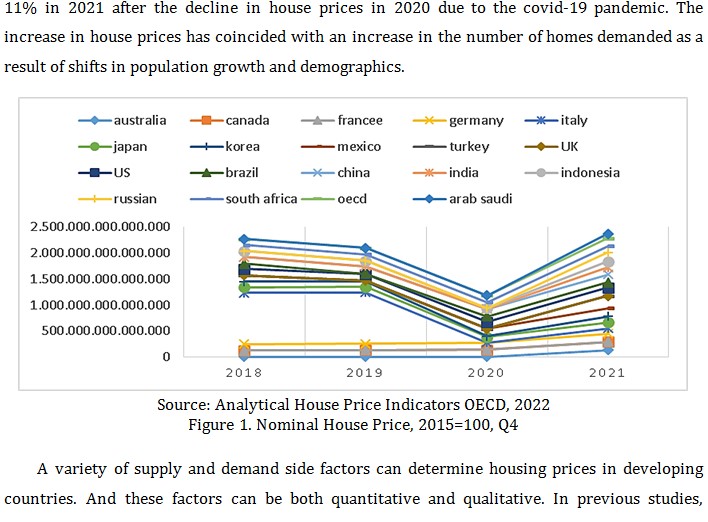
A house or a place to live is a primary need for all beings, but the lack of affordable housing to buy or rent can trigger a global housing crisis. After the collapse of the housing market in the US or the subprime crisis of 2008-2009 there was a revival of focus on the housing market. Empirical research has been conducted to look at the variables that affect house prices. However, it is still rare for researchers to examine the influence of macroeconomic variables in countries that have a strong role in the world economy. Therefore this study aims to determine the effect of the Consumer Price Index, Construction GDP, Unemployment Rate, Population Density, Exchange Rate and Power Purchasing Parity on the House Price Index as an indicator that reflects house prices. So, the contribution of this research is to provide novelty in the use of the house price index to determine the determinants that influence it. This research is a quantitative research using secondary data. The regression model used in this study is the Random Effects Model. The result of this study is the Consumer Price Index and Purchasing Power Parity have a significant positive impact on house prices. Therefore, the government needs to maintain the stability of these two indicators so that house prices remain stable. The Unemployment Rate and Exchange Rate show a significant negative effect on house prices. Therefore, the government needs to monitor and maintain the stability of the exchange rate and reduce the unemployment rate so that there is no significant decline in house prices. Meanwhile, construction GDP and population density show no effect on house prices. Additional studies are urgently needed to identify factors and housing price movements contributing to global and regional levels.
References
Balqis, S. F., & Purwono, R. (2021). Determinant of Residential Property Price Index in Five Asian Emerging Market Countries: A Demand and Supply Approach. International Journal of Social Science and Economics Invention, 07(08), 169-177. doi:https://doi.org/10.23958/ijssei/vol07-i08/313
Belke, A., & Keil, J. (2018). Fundamental Determinants of Real Estate Prices: A Panel Study of German Regions. In International Advances in Economic Research (Vol. 24, Issue 1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11294-018-9671-2
Budi, R. S. (2021). Hubungan Jangka Panjang Dan Jangka Pendek Variabel Makroekonomi Yang Mempengaruhi Harga Berbagai Tipe Rumah Di Indonesia. Jurnal Manajemen Aset Dan Penilai, 1(2), 1–10. http://jmap.mappi.or.id/index.php/journal-penilai/article/view/13%0Ahttps://jmap.mappi.or.id/index.php/journal-penilai/article/download/13/9
Çalıyurt, O. (2022). The Mental Health Consequences of the Global Housing Crisis. PMC PubMed Central, 23(6), 264-265. doi:https://doi.org/10.5152%2Falphapsychiatry.2022.17112022
Chappell, S. C. (2014). Market analysis. In Principles of Pharmaceutical Marketing. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315859774
Cohen, V., & Karpavičiūtė, L. (2017). The Analysis of The Determinants of Housing Prices. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 8(1), 49-63. doi:10.14807/ijmp.v8i1.521
Everett-Allen, K. (2021). Global Residential Cities Index Q2 2021. Knight Frank, 2. https://content.knightfrank.com/research/1026/documents/en/global-residential-cities-index-q2-2021-8453.pdf
Fanama, V., & Pratikto, R. (2019). Bubble Property Di Indonesia: Analisis Empiris Survei Harga Properti Residensial. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis, 15(2), 169–180.
Fauzia, L. R. (2019). Determinan Harga Rumah di Indonesia. DINAMIKA: Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan, 11(1), 61–68.
Georgieva, K. (2022, July 13). Facing a Darkening Economic Outlook: How the G20 Can Respond. Retrieved June 22, 2023, from IMF Blog: https://www.imf.org/en/Blogs/Articles/2022/07/13/blog-how-g20-can-respond
Glaeser, E. L., Gyourko, J., & Saks, R. E. (2005). Why have housing prices gone up? American Economic Review, 95(2), 329–333. https://doi.org/10.1257/000282805774669961
Glindro, E. T., Subhanij, T., Szeto, J., & Zhu, H. (2011). Determinants of house prices in nine Asia-Pacific economies. International Journal of Central Banking, 7(3), 163–204. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1333646
Graham, J., & Makridis, C. A. (2023). House Prices and Consumption: A New Instrumental Variables Approach. American Economic Journal: Macroeconomics, 15(1), 411-43. doi:10.1257/mac.20200246
Hikam, A. A. (2021). Analisis Determinan Harga Properti Berdasarkan Tingkat Investasi Di 5 Negara Asia. Nuevos Sistemas de Comunicación e Información, 2013–2015.
Hilber, C. A. L., & Vermeulen, W. (2016). The Impact of Supply Constraints on House Prices in England. Economic Journal, 126(591), 358–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecoj.12213
Ho, W. K. O., & Ganesan, S. (1998). ON LAND SUPPLY AND THE PRICE OF RESIDENTIAL HOUSING. Netherlands Journal of Housing and the Built Environment, 13(4), 439–452. http://www.jstor.org/stable/41107764
Kemenlu, K. L. (2022, March 23). Getting to Know the G20 and Indonesia Hold the G20 Presidency in 2022. Retrieved from Consulate General of The Republic of Indonesia In Guangzhou, The People's Republic of China: https://kemlu.go.id/guangzhou/en/news/18078/getting-to-know-the-g20-and-indonesia-hold-the-g20-presidency-in-2022
Li, C. (2015). Analysis of Influence Factors for Chinese Housing Prices Based on The Factor Analysis Method. International Conference on Engineering Management, Engineering Education and Information Technology, 552-555.
Leung, C. (2004). Macroeconomics and housing: A review of the literature. Journal of Housing Economics, 13(4 SPEC.ISS.), 249–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhe.2004.09.002
Ma, L., Liu, C., & Reed, R. (2017). The impacts of residential construction and property prices on residential construction outputs: an inter-market equilibrium approach. International Journal of Strategic Property Management, 21(3), 296–306. https://doi.org/10.3846/1648715X.2016.1255675
Magdalena. (2015). The Effect of Interest Rates and Exchange Rates on The Residential Property Price Index Residential Property Price Index (IHPR) in Indonesia 2022-2013. Ultima management, 7(1), 1-13
Mahalik, M. K., & Mallick, H. (2011). What causes asset price bubble in an emerging economy? some empirical evidence in the housing sector of India. International Economic Journal, 25(2), 215–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10168737.2011.586806
Mohan, S., Hutson, A., MacDonald, I., & Lin, C. C. (2019). Impact of macroeconomic indicators on housing prices. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, 12(6), 1055–1071. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-09-2018-0070
Mankiw, N. G. (2015). Principles of Microeconomics. USA: Cengage Learning.
Nakajima, M. (2011). Understanding House-Price Dynamics. Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Review, 20–28. http://www.phil.frb.org/econ/br/index.html%5Cnhttp://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=ecn&AN=1282013&site=ehost-live&scope=site
Nistor, A., & Reianu, D. (2018). Determinants of Housing Prices: Evidence from Ontario Cities, 2001-2011. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, 11(3), 541-556.
Panagiotidis, T., & Printzis, P. (2016). On the macroeconomic determinants of the housing market in Greece: a VECM approach. International Economics and Economic Policy, 13(3), 387–409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10368-016-0345-3
Pinjaman, S., & Kogid, M. (2020). Macroeconomic determinants of house prices in Malaysia. Jurnal Ekonomi Malaysia, 54(1), 153–165. https://doi.org/10.17576/JEM-2020-5401-11
Posfai, Zsuzsanna., Nagy, Gabor. (2017). Crisis and The Reproduction of Core-Periphery Relations on The Hungarian Housing Market. European Spatial Research and Policy. 24(2), 17-38
Schiller, Robert. (2000). Irrational Exhuberance.
Solving the global housing crisis|World Finance. (n.d.). https://www.worldfinance.com/infrastructure-investment/solving-the-global-housing-crisis
Sumer, Levent., Ozorhan, Beliz. (2020). The Exchange Rate Effect on Housing Price Index and Reit Index Return Rates. Finansial Arastirmalar ve Calismalar, 12(22), 249-266. https://doi.org/10.14784/marufacd.688468
Tripathi, Sabyasachi. (2019). Macroeconomic Determinants of Housing Prices: A Cross Country Level Analysis. Munich Personal Repec Archive, 1-17.
Wang, J. J., Chen, P., Croucher, J. S., & Tiwari, P. (2020). Long-Term and Short-Term House Price Dynamics in China’s First Tier and Second Tier Main 13 Cities. Chinese Economy, 53(1), 62–81. https://doi.org/10.1080/10971475.2019.1625517
Xu, L., & Tang, B. (2014). On The Determinants of UK House Prices. International Journal of Economics and Research, 5(2), 57–64. www.ijeronline.com
Yao, R., & Zhang, H. H. (2005). Optimal consumption and portfolio choices with risky housing and borrowing constraints. Review of Financial Studies, 18(1), 197–239. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhh007
Zhang, Z. (2021). Analysis on the Influencing Factors and Causes of China's High Housing Prices. Advances in Economics, Business and Management Research, 166, 254-258.
Zamillaili, M., & Qoyum, A. (2021). Determinasi Harga Perumahan di Indonesia dan Malaysia.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Ignatius Abasimi, Anisa Rupaningtyas Aulia, Uswatun Khasanah

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.












