Modelling the Drivers of Housing Price using Autoregressive Distributed Lag – Error Correction Model (ARDL-ECM) in Indonesia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/jampe.v2i1.6696Keywords:
ARDL-ECM , Housing Market , Housing Price , Macroeconomic Drivers , ModellingAbstract
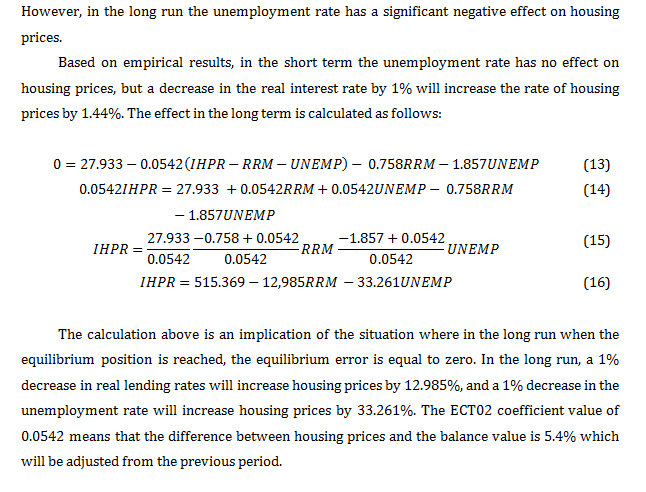
This study aims to design a model tand to estimate the effect of market fundamentals (macroeconomic drivers) on housing prices in Indonesia. The identification of macroeconomic drivers helps the government utilize these macroeconomic indicators to control housing prices in accordance with the current situation. Therefore, the contribution of this study is to analyse how is the housing price in Indonesia. The analytical tool used in this study is the Autoregressive Distributed Lag-Error Correction Model (ARDL-ECM). The variables used in this study are the residential housing price index, real loan interest rates, and the unemployment rate with the observation period starting in the first quarter of 2010 - fourth quarter of 2019. The process of establishing the ARDL-ECM was carried out through a series of tests on research data. Based on the ARDL-ECM estimation results, it was found that in the short-term real loan interest rates had a negative and significant effect on housing prices, while in the long-term real loan interest rates and unemployment rates had a negative and significant effect on housing prices. These results indicate that real interest rates and unemployment rates as macroeconomic drivers can affect housing prices so that they can be utilized by policy makers, specifically through monetary policy (interest rates) and fiscal policy (unemployment rate).
References
Abelson, P., Joyeux, R., Milunovich, G., dan Chung, D. (2005). Explaining house price in Australia: 1970-2003. The Economic Record, Vol. 81 No. S1, 96 – 103. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-4932.2005.00243.x
Al-Masum, M. A., dan Lee, C. L. (2018). Modelling housing prices and market fundamentals: evidence from the Sydney housing market. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, Vol. 12 No. 4, 746 – 762. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-10-2018-0082
Asal, M. (2017). Long-run drivers and short-term dynamics of Swedish real houses prices. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, Vol. 11 No. 1, 45 - 72. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-08-2017-0070
Bjonland, H. C., dan Jacobsen, D. H. (2010). The role of house prices in the monetary policy transmission mechanism in small open economies. Journal of Financial Stability, Vol. 6 No. 4, 218 – 229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfs.2010.02.001
Chi-Wei, S., Yin, X. C., Tao, R., dan Zhou, H. (2017). Are housing prices improving GDP or vice versa? A cross-regional study of China. Applied Economics, Vol. 50 No. 29, 3171–3184. doi:10.1080/00036846.2017.1418078. https://doi.org/10.1080/00036846.2017.1418078
Claussen, C. A. (2013). Are Swedish houses overpriced?. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, Vol. 6 No. 2. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-12-2011-0056
Égert, B., dan Mihaljek, D. (2007). Determinants of House Prices in Central and Eastern Europe. William Davidson Institute Working Paper Number 894. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.ces.8100221
Insukindro. (1991). Regresi Linier Lancung dalam Analisis Ekonomi: Suatu Tinjauan dengan Satu Studi Kasus di Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis Indonesia, Vol 6, 75-87
Li, Q., dan Chand, S. (2013). House prices and market fundamentals in urban China. Habitat International 40, 148 – 153. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2013.04.002
Miller, N., Peng, L. dan Sklarz, M. (2011). House Price and Economic Growth. J Real Estate Finan Econ 42:522 – 541 Speringer Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11146-009-9197-8
Miregi, M. O., dan Obere, A. (2014). Effects of Market Fundamental Variables on Property Prices in Kenya – A Case of Nairobi Residential Property Market. IOSR Journal of Economics and Finance. https://doi.org/10.9790/5933-055101113
Mohan, S., Hutson, A., Macdonald, I., dan Lin, C. C. (2019). Impact of Macroeconomic Indicators on Housing Prices. International Journal of Housing Markets and Analysis, Vol. 12 No. 6, 1055 - 1071. Emerald Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJHMA-09-2018-0070
Ozmen, M. U., Kalafatcilar, M. K., dan Yulmaz, E. (2019). The Impact of Income Distribution on House Prices. Central Bank Review 19, 45 - 58. Central Bank of The Republic of Turkey. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbrev.2019.05.001
Wyatt P. (2013). Property valuation, 2e. John Wiley dan Sons dan Blackwell.
Shrestha, M. B., dan Bhatta, G. R. (2018). Selecting appropriate methodological framework for time series data analysis. The Journal of Finance and Daa Science, 1 – 17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfds.2017.11.001
Sivitanides, P. S. (2018). Macroeconomic drivers of London house price. Journal of Property Investment dan Finance, Vol. 36 No.6. Emerald Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1108/JPIF-02-2018-0012
Stevenson, S. (2008). Modelling Housing Market Fundamentals: Empirical Evidence of Extreme Market Condition. Real Estate Economics V36 American Real Estate and Urban Economics Association. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6229.2008.00204.x
Thomas, R. L. (1997). Modern Econometrics an Introduction. Addison-Wesley.
Whelan, J., dan Msefer, K. (1994). Economic Supply dan Demand. MIT Sustem Dynamics in Education Project.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Bagaskara

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.












