Forensik Web Layanan Instant Messaging Menggunakan Metode Association of Chief Police Officers
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.12928/mf.v1i1.705Abstract
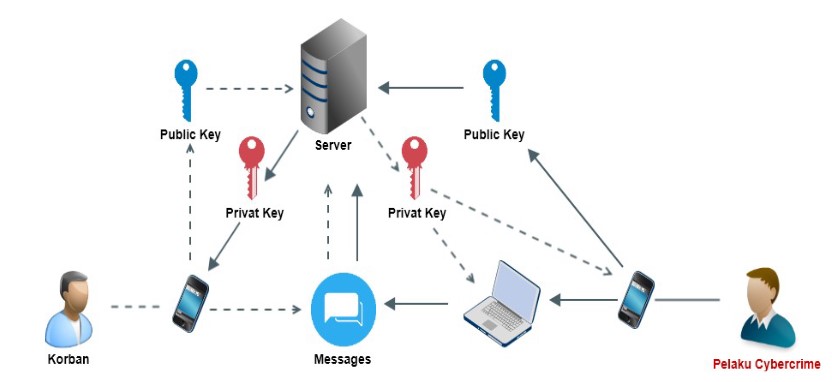
Aplikasi instant messaging khususnya yang terdapat layanan berbasis web, sangat memungkinkan untuk dijadikan sasaran oleh para pelaku tindak kejahatan digital atau cybercrime. Vulnerabilitas dari aplikasi instant messaging berbasis web dapat dieksploitasi oleh pihak-pihak yang tidak bertanggung jawab untuk melakukan tindak kejahatan digital. Penelitian ini difokuskan pada tahapan-tahapan investigasi forensik kasus tindak kejahatan digital yang terjadi di layanan berbasis web aplikasi instant messaging WhatsApp, LINE dan Telegram. Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini merujuk pada metode Association of Chief Police Officers dengan alur plan, capture, analyse dan present. Penelitian ini dalam proses investigasi forensiknya berhasil didapatkan artifact dari layanan berbasis web aplikasi instant messaging. Alat atau tools investigasi forensik yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah FTK imager, NetWitness Investigator, dan Wireshark. Tingkat kerberhasilan penelitian ini mencapai 40% pada aplikasi Telegram, 60% untuk aplikasi LINE, dan aplikasi WhatsApp yang menduduki pringkat tertinggi dengan tingkat keberhasilan sebesar 85%.
References
Actoriano, B., & Riadi, I. (2018). Forensic Investigation on Whatsapp Web Using Framework Integrated Digital Forensic Investigation on Whatsapp Web Using Framework Integrated Digital Forensic Investigation Framework Version 2, (September).
Anwar, N., & Riadi, I. (2017). Analisis Investigasi Forensik WhatsApp Messanger Smartphone Terhadap WhatsApp Berbasis Web. Jurnal Ilmiah Teknik Elektro Komputer Dan Informatika, 3(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.26555/jiteki.v3i1.6643
Asyaky, M. S. (2019). Analisis dan Perbandingan Bukti Digital Aplikasi Instant Messenger Pada Android, 3(October).
Aziz, M. A., Riadi, I., & Umar, R. (2018). Menggunakan Framework National Institute of Justice, 2018(November), 51-57.
Chang, M. S., & Chang, C. Y. (2018). Forensic Analysis of LINE Messenger on Android. Journal of Computers, 29(1), 11-20. https://doi.org/10.3966/199115992018012901002
Faiz, M. N., Umar, R., & Yudhana, A. (2017). Implementasi Live Forensics untuk Perbandingan Browser pada Keamanan Email. JISKa, 1(February), 108-114. https://doi.org/10.14421/jiska.2017.13-02
Fauzan, A., Riadi, I., & Fadlil, A. (2017). Analisis Forensik Digital Pada Line Messenger Untuk Penanganan Cybercrime. Annual Research Seminar (ARS), 2(1), 159-163. Retrieved from http://seminar.ilkom.unsri.ac.id/index.php/ars/article/view/832/752
Kukuh, M., & Haryanto, T. (2018). Analisa Forensics Terhadap Database Sqlite pada Aplikasi IMO Berbasis Android.
Madiyanto, S., Mubarok, H., & Widiyasono, N. (2017). Mobile Forensics Investigation Proses Investigasi Mobile Forensics Pada Smartphone Berbasis IOS. Jurnal Rekayasa Sistem & Industri (JRSI), 4(01). https://doi.org/10.25124/jrsi.v4i01.149
Riadi, I., Fadlil, A., & Fauzan, A. (2018). Evidence Gathering and Identification of LINE Messenger on Android Device. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security (IJCSIS), 16(June), 201-205.
Riadi, I., & Rauli, E. (2018). Identifikasi Bukti Digital WhatsApp pada Sistem Operasi Proprietary Menggunakan Live Forensics. Scientific Journal of Informatics (SJI) UNNES, 10(1), 18-22.
Riadi, I., Sunardi, S., & Fauzan, A. (2018). Examination of Digital Evidence on Android-based LINE Messenger. International Journal of Cyber-Security and Digital Forensics (IJCSDF), 7(3), 337-343.
Riadi, I., Umar, R., & Nasrulloh, I. M. (2018). Analisis Forensik Digital Pada Frozen Slod State Drive Dengan Metode National Institute of Justice ( Nij ), 3(May), 70-82. https://doi.org/10.21831/elinvo.v3i1.19308
Riadi, I., Yudhana, A., Caesar, M., & Putra, F. (2018). Akuisisi Bukti Digital Pada Instagram Messenger Berbasis Android Menggunakan Metode National Institute Of Justice ( NIJ ), 4, 219-227.
ThreatMetrix. (2018). Q2 2018 Cybercrime Report, 2018(June), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.14084/j.cnki.cn62-1185/c.2018.02.021
Umar, R., Riadi, I., & Maulana, G. (2017). A Comparative Study of Forensic Tools for WhatsApp Analysis using NIST Measurements. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications, 8(12), 69-75. https://doi.org/10.14569/IJACSA.2017.081210
Yusoff, M. N., Dehghantanha, A., & Mahmod, R. (2017). Forensic Investigation of Social Media and Instant Messaging Services in Firefox OS. Contemporary Digital Forensic Investigations of Cloud and Mobile Applications, 41-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-805303-4.00004-6
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2019 Imam Riadi, Rusydi Umar, Muhammad Abdul Aziz

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Start from 2019 issues, authors who publish with JURNAL MOBILE AND FORENSICS agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY-SA 4.0) that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgment of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.












 Mobile and Forensics (MF)
Mobile and Forensics (MF)